CAF: Call Legs Resync
(→Re-sync timeout) |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Since the [[Toolpack]] framework has been designed for HA ([[High_Availability_Overview]]), it's mandatory that an application that manage calls through [[CAF_Call_interface]] is able to deal with call legs re-synchronization. | Since the [[Toolpack]] framework has been designed for HA ([[High_Availability_Overview]]), it's mandatory that an application that manage calls through [[CAF_Call_interface]] is able to deal with call legs re-synchronization. | ||
| − | The current page contains an overview of how re-synchronization works. For more details, please refer to the following page: | + | The current page contains an overview of how re-synchronization works. For more details, please refer to the following section of the this page: |
[[CAF:_Working_With_Caf_Call_Legs#Re-synchronizing_with_toolpack_engine]] | [[CAF:_Working_With_Caf_Call_Legs#Re-synchronizing_with_toolpack_engine]] | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
=== CAF application === | === CAF application === | ||
| − | The call control application | + | The CAF call control application that was disconnected from [[Toolpack_Application:toolpack_engine|toolpack_engine]] will update (or re-build) it's call leg contexts by getting information automatically pushed by [[Toolpack_Application:toolpack_engine|toolpack_engine]] upon re-connection. |
All active (answered) calls will be re-synchronized from [[Toolpack_Application:toolpack_engine|toolpack_engine]]. | All active (answered) calls will be re-synchronized from [[Toolpack_Application:toolpack_engine|toolpack_engine]]. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
== Example scenarios == | == Example scenarios == | ||
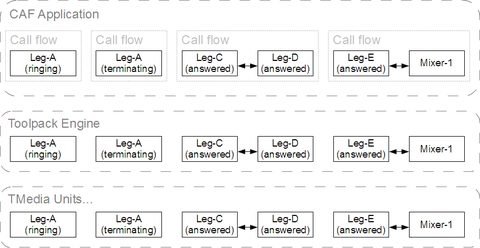
| + | [[Image:CAFCallFlow_examples_initial.png|thumb|480px|Example scenario: Initial state]] | ||
| + | |||
In all the scenarios below, let's consider the following situation: | In all the scenarios below, let's consider the following situation: | ||
| − | * | + | * Leg-A: Ringing |
| + | * Leg-B: Terminating | ||
| + | * Leg-C: Active (answered) | ||
| + | * Leg-D: Active (answered) | ||
| + | * Leg-E: Active (answered) | ||
| + | * Leg-C and Leg-D are joined (connected) together | ||
| + | * Mixer-1: Ready | ||
| + | * Leg-E and Mixer-1 are joined (connected) | ||
| + | |||
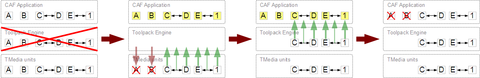
| + | === Scenario 1: toolpack_engine quickly restarted === | ||
| + | [[Image:CAFCallFlow_examples_scenario_1.png|thumb|480px|Example scenario 1]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * CAF Application is notified | ||
| + | ** ''OnCmcLibNotReady()'' | ||
| + | ** ''OnSyncLost()'' for Leg-A, Leg-B, Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E | ||
| + | ** ''OnMixerSyncLost()'' on Mixer-1 | ||
| + | * toolpack_engine restarts | ||
| + | ** Queries information from all TMedia units | ||
| + | ** Drop incomplete legs and mixers (here Leg-A and Leg-B) | ||
| + | ** Re-build contexts for active legs and mixers (here Leg-C, Leg-D, Leg-E and Mixer-1) | ||
| + | ** Re-build connections between legs/mixers (here Leg-C with Leg-D, Leg-E with Mixer-1) | ||
| + | * toolpack_engine pushes information to CAF library: | ||
| + | ** Legs: Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E | ||
| + | ** Mixers: Mixer-1 | ||
| + | ** Connections: Leg-C with Leg-D, Leg-E with Mixer-1 | ||
| + | * CAF library compares with it's own contexts: | ||
| + | ** ''OnCallLegTerminated()'' for Leg-A and Leg-B | ||
| + | ** ''OnSyncDone()'' for Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E | ||
| + | ** ''OnMixerSyncDone()'' for Mixer-1 | ||
| + | * Ready to continue | ||
| + | ** ''OnCmcLibReady()'' | ||
| + | |||
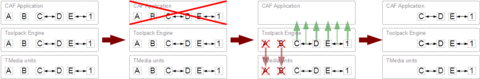
| + | === Scenario 2: toolpack_engine stopped (disconnected) for more than 10 seconds === | ||
| + | [[Image:CAFCallFlow_examples_scenario_2.png|thumb|480px|Example scenario 2]] | ||
| + | * CAF Application is notified | ||
| + | ** ''OnCmcLibNotReady()'' | ||
| + | ** ''OnSyncLost()'' for Leg-A, Leg-B, Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E | ||
| + | ** ''OnMixerSyncLost()'' on Mixer-1 | ||
| + | (... 10 seconds elapse...) | ||
| + | * CAF Application declares toolpack_engine "dead", destroys all it's local contexts: | ||
| + | ** ''OnCallLegTerminated()'' for all legs: Leg-A, Leg-B, Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E | ||
| + | ** ''OnMixerTerminated()'' for all mixers: Mixer-1 | ||
| + | (... some time elapse...) | ||
| + | * toolpack_engine is restarted | ||
| + | ** Queries information from all TMedia units | ||
| + | ** Drop incomplete legs and mixers (here Leg-A and Leg-B) | ||
| + | ** Re-build contexts for active legs and mixers (here Leg-C, Leg-D, Leg-E and Mixer-1) | ||
| + | ** Re-build connections between legs/mixers (here Leg-C with Leg-D, Leg-E with Mixer-1) | ||
| + | * toolpack_engine pushes information to CAF library: | ||
| + | ** Legs: Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E | ||
| + | ** Mixers: Mixer-1 | ||
| + | ** Connections: Leg-C with Leg-D, Leg-E with Mixer-1 | ||
| + | * CAF library compares with it's own contexts (none!): | ||
| + | ** ''OnCallLegSync()'' for Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E | ||
| + | *** Application may refuse them: ''RefuseLeg()'' | ||
| + | *** Application may re-allocate new contexts for these legs | ||
| + | ** ''OnMixerSync()'' for Mixer-1 | ||
| + | *** Application may refuse: ''RefuseMixer()'' | ||
| + | *** Application may re-allocate new contexts for these mixers | ||
| + | ** ''OnLinkSync()'' for Leg-C with Leg-D | ||
| + | *** Application may refuse: ''RefuseLink()'' | ||
| + | *** Application may re-allocate new "call flow" contexts, re-bind legs to them (''BindCallLeg'') | ||
| + | ** ''OnMixerLinkSync()'' for Leg-E with Mixer-1 | ||
| + | *** Application may refuse: ''RefuseMixerLink()'' | ||
| + | *** Application may re-allocate new "call flow" contexts, re-bind legs/mixers to them (''BindCallLeg'', ''BindMixer'') | ||
| + | * Ready to continue | ||
| + | ** ''OnCmcLibReady()'' | ||
| − | + | === Scenario 3: CAF application is restarted === | |
| + | [[Image:CAFCallFlow_examples_scenario_3.png|thumb|480px|Example scenario 3]] | ||
| + | * If the application is quitting in a 'clean' manner | ||
| + | ** 'OnLegFreed()' is called for all call legs (Leg-A, Leg-B, Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E) | ||
| + | ** Destructor of all call flows is called | ||
| + | * When the application is restarted | ||
| + | ** => This is exactly same scenario as the end of Scenario 2 after step 'toolpack_engine pushes information to CAF library'. | ||
= For more information... = | = For more information... = | ||
Latest revision as of 06:32, 23 January 2014
Contents |
Call Legs Resynchronization
Since the Toolpack framework has been designed for HA (High_Availability_Overview), it's mandatory that an application that manage calls through CAF_Call_interface is able to deal with call legs re-synchronization.
The current page contains an overview of how re-synchronization works. For more details, please refer to the following section of the this page:
CAF:_Working_With_Caf_Call_Legs#Re-synchronizing_with_toolpack_engine
Situations where call leg resynchronization is required
Call legs re-synchronization is required whenever the CAF application looses communication with toolpack_engine:
- The CAF application was restarted
- The toolpack_engine was restarted
- Network connection between CAF application and toolpack_engine was momentarily down
General principles of call legs re-sync
Toolpack Engine
The toolpack_engine application, when restarted, will re-build it's call leg contexts by querying information on the TMedia Units.
- Transient calls (not yet answered) will be dropped
- Terminating calls will be dropped
- Active (answered) calls will be re-build like they were before toolpack_engine was restarted
CAF application
The CAF call control application that was disconnected from toolpack_engine will update (or re-build) it's call leg contexts by getting information automatically pushed by toolpack_engine upon re-connection.
All active (answered) calls will be re-synchronized from toolpack_engine.
- Calls already known by the application will remain valid
- Calls unknown by the application will be re-constructed (or refused): OnCallLegSync, OnLinkSync
- Calls known by the application, but no more present in toolpack_engine are terminated: OnCallLegTerminated
Example scenarios
In all the scenarios below, let's consider the following situation:
- Leg-A: Ringing
- Leg-B: Terminating
- Leg-C: Active (answered)
- Leg-D: Active (answered)
- Leg-E: Active (answered)
- Leg-C and Leg-D are joined (connected) together
- Mixer-1: Ready
- Leg-E and Mixer-1 are joined (connected)
Scenario 1: toolpack_engine quickly restarted
- CAF Application is notified
- OnCmcLibNotReady()
- OnSyncLost() for Leg-A, Leg-B, Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E
- OnMixerSyncLost() on Mixer-1
- toolpack_engine restarts
- Queries information from all TMedia units
- Drop incomplete legs and mixers (here Leg-A and Leg-B)
- Re-build contexts for active legs and mixers (here Leg-C, Leg-D, Leg-E and Mixer-1)
- Re-build connections between legs/mixers (here Leg-C with Leg-D, Leg-E with Mixer-1)
- toolpack_engine pushes information to CAF library:
- Legs: Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E
- Mixers: Mixer-1
- Connections: Leg-C with Leg-D, Leg-E with Mixer-1
- CAF library compares with it's own contexts:
- OnCallLegTerminated() for Leg-A and Leg-B
- OnSyncDone() for Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E
- OnMixerSyncDone() for Mixer-1
- Ready to continue
- OnCmcLibReady()
Scenario 2: toolpack_engine stopped (disconnected) for more than 10 seconds
- CAF Application is notified
- OnCmcLibNotReady()
- OnSyncLost() for Leg-A, Leg-B, Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E
- OnMixerSyncLost() on Mixer-1
(... 10 seconds elapse...)
- CAF Application declares toolpack_engine "dead", destroys all it's local contexts:
- OnCallLegTerminated() for all legs: Leg-A, Leg-B, Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E
- OnMixerTerminated() for all mixers: Mixer-1
(... some time elapse...)
- toolpack_engine is restarted
- Queries information from all TMedia units
- Drop incomplete legs and mixers (here Leg-A and Leg-B)
- Re-build contexts for active legs and mixers (here Leg-C, Leg-D, Leg-E and Mixer-1)
- Re-build connections between legs/mixers (here Leg-C with Leg-D, Leg-E with Mixer-1)
- toolpack_engine pushes information to CAF library:
- Legs: Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E
- Mixers: Mixer-1
- Connections: Leg-C with Leg-D, Leg-E with Mixer-1
- CAF library compares with it's own contexts (none!):
- OnCallLegSync() for Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E
- Application may refuse them: RefuseLeg()
- Application may re-allocate new contexts for these legs
- OnMixerSync() for Mixer-1
- Application may refuse: RefuseMixer()
- Application may re-allocate new contexts for these mixers
- OnLinkSync() for Leg-C with Leg-D
- Application may refuse: RefuseLink()
- Application may re-allocate new "call flow" contexts, re-bind legs to them (BindCallLeg)
- OnMixerLinkSync() for Leg-E with Mixer-1
- Application may refuse: RefuseMixerLink()
- Application may re-allocate new "call flow" contexts, re-bind legs/mixers to them (BindCallLeg, BindMixer)
- OnCallLegSync() for Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E
- Ready to continue
- OnCmcLibReady()
Scenario 3: CAF application is restarted
- If the application is quitting in a 'clean' manner
- 'OnLegFreed()' is called for all call legs (Leg-A, Leg-B, Leg-C, Leg-D and Leg-E)
- Destructor of all call flows is called
- When the application is restarted
- => This is exactly same scenario as the end of Scenario 2 after step 'toolpack_engine pushes information to CAF library'.
For more information...
The current page contains an overview of how re-synchronization works. For more details, please refer to the following page:
CAF:_Working_With_Caf_Call_Legs#Re-synchronizing_with_toolpack_engine