SIP Registration
William Wong (Talk | contribs) |
William Wong (Talk | contribs) (→Configuration) |
||
| (49 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | SIP | + | == SIP Registrar == |
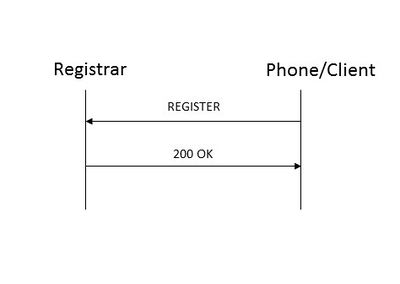
| + | A SIP [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Session_Initiation_Protocol#Registrar registrar]’s role is to accept REGISTER requests with an Address Of Record (URI) and write the associated contact bindings to a location service. The location service is a logical entity and is simply a database that contains a list of AOR to contact address bindings. Very often a registrar functions as a location service. It is also very common for a registrar/location service to be co-located with the proxy server for the same domain. The example below shows a typical registration transaction. | ||
| + | [[Image:SIP Registration Process.jpg|400px]] | ||
| − | + | Tmedia supports two modes for SIP Registration: | |
| − | The | + | * The Tmedia forwards per-user registration requests from users |
| + | ** [[Sip_registration_forwarding|Explanation of Tmedia's registration forwarding]] | ||
| + | ** [[Toolpack:Creating_a_SIP_Domain_SBC_A|Configuration of Tmedia's registration forwarding]] | ||
| + | * The Tmedia registers itself to the SIP Proxy (per SIP NAP, as explained below in current page) | ||
| + | == Registration per SIP NAP == | ||
| + | The Tmedia supports to register a SIP [[NAP]] to a SIP proxy. Registration, can be used, for example, to authenticate the Tmedia Gateway IP address to a SIP provider proxy or SBC and allow the SIP traffic from the Tmedia to that SIP provider. | ||
| + | * Registration is when Tmedia sends a SIP REGISTER to a Registrar, and gets a response which could be accepted (200 OK) or refused (4xx reason code). Upon refusal, the registration is not stopped and is retried after 5 seconds. | ||
| + | * Even if there is no call on the system, Tmedia will send SIP REGISTER | ||
| + | * Sending SIP REGISTER will happen when the option [[Parameter:_Register_to_Proxy|"Register to Proxy?"]] is selected for a specific SIP [[NAP]] | ||
| + | * If you apply a new configuration and the option [[Parameter:_Register_to_Proxy|"Register to Proxy?"]] is present it will start sending SIP REGISTER | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Register with no answer from registrar === | |
| + | If it is not registered already, the Tmedia will send a new SIP REGISTER every 32 + 5 seconds interval until it receive a response from the Registrar | ||
| + | *Over UDP (shown it the message flow bellow), the REGISTER request is retransmitted for 32 seconds before the request transaction timeout, then a new SIP REGISTER is sent after 5 seconds. | ||
| + | *Over TCP, if the SIP registrar does not listen on the TCP port, a new TCP connection is retried every 5 seconds. If the TCP connection is established but no SIP responses returned by the Registrar, the transaction timeout after 32s and then a new SIP REGISTER is sent after 5 seconds. | ||
| + | [[Image:SIP_Register_no_answers.png|500px]] | ||
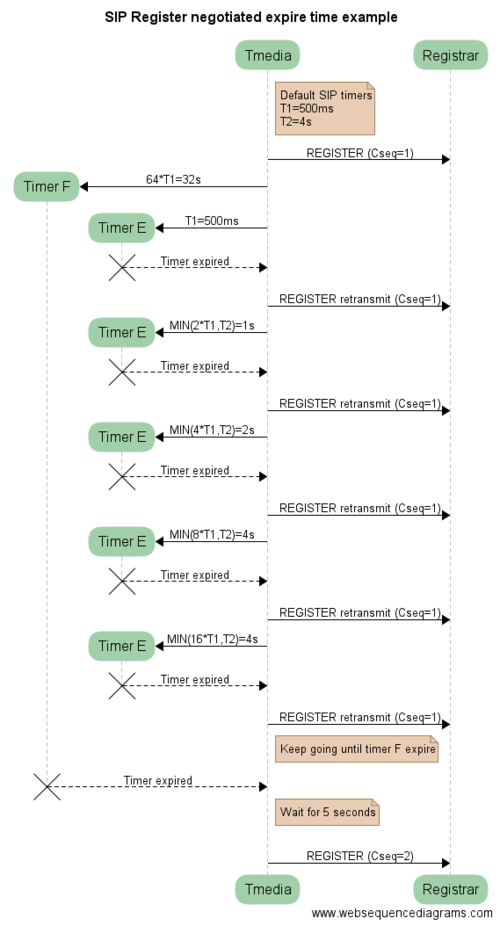
| − | + | ===Register expire negotiation === | |
| + | The REGISTER request negotiate the contact binding expiration by adding "expires=3600" parameter to the contact header. The value is hardcoded to 3600 seconds. | ||
| + | If the REGISTER response from the Registrar does not change the "expires" parameter: | ||
| + | * The SIP REGISTER will be "valid" for 3600 seconds | ||
| + | * Tmedia will send a new REGISTER (to refresh the registration) after half of the minimum registration negotiated, general use will be at 1800 seconds (3600/2) | ||
| + | The Registrar can change the "expires" contact parameter or the Expires header as shown in the two example below to negotiate a value different from 3600 seconds. | ||
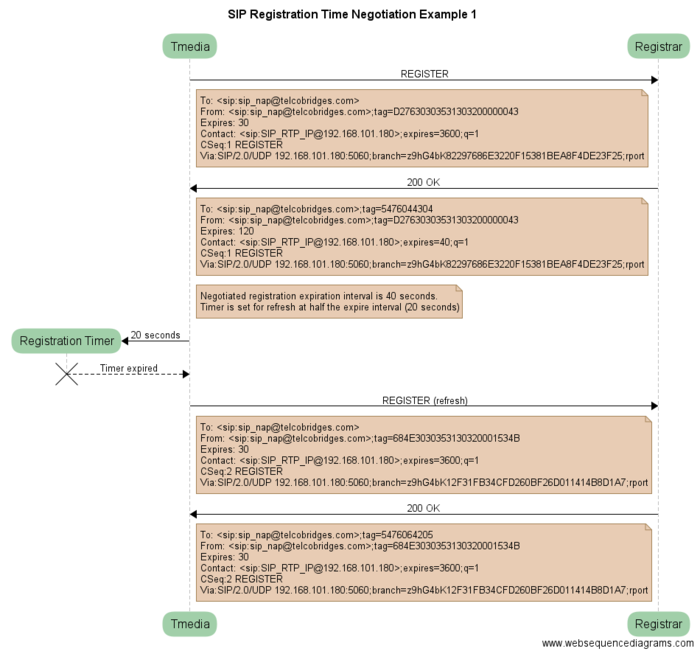
| + | ==== Negotiation uses case 1: contact expires header ==== | ||
| + | In the example below, the Registrar changes the "expires" contact parameter. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:SIP_Register_negotiated_expire_time_example_1.png|700px]] | |
| − | + | ||
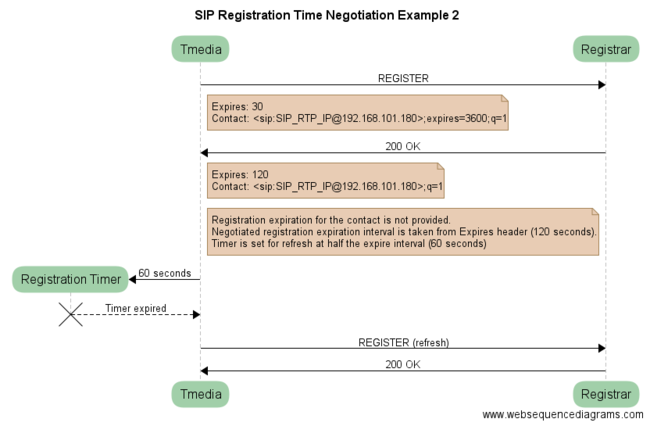
| + | ==== Negotiation uses case 2: no contact expires parameter; Expires header ==== | ||
| + | In the example below, the Registrar removes the "expires" contact parameter and set the Expires header. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:SIP Register negotiated expire time example 2.png|650px]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
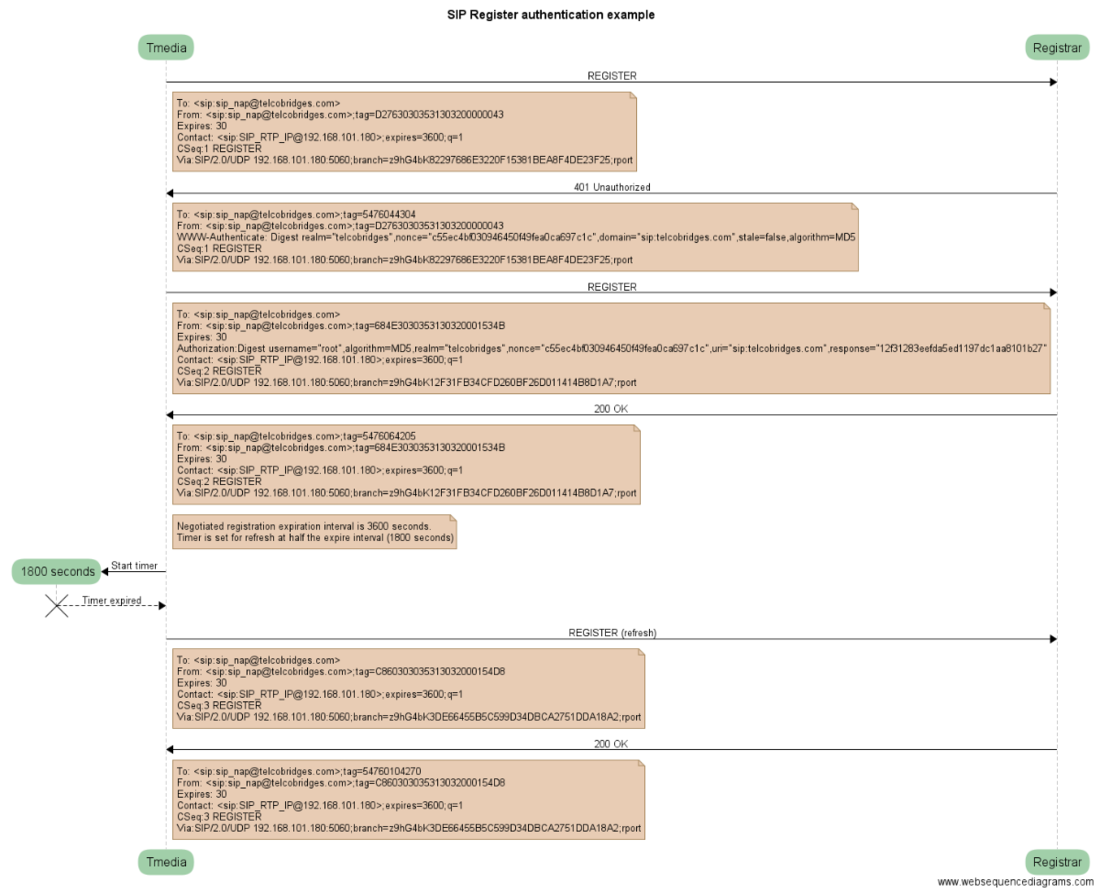
| + | ===Register Authentication=== | ||
| + | * If Authentication is required, the Registrar returns a 401 Unauthorized response with a WWW-Authenticate header | ||
| + | * The WWW-Authenticate header contains nonce to encrypt user’s communications password, user then sends a second REGISTER containing an Authorization header with the user's encrypted password | ||
| + | [[Image:SIP_Register_401_authentication_example.png|1100px]] | ||
== Configuration == | == Configuration == | ||
| − | *[[Toolpack: | + | *[[Toolpack:Allocating a SIP Network Access Point (NAP) F|Allocating a SIP NAP Configuration v3.0]] |
| − | *[[Toolpack: | + | *[[Toolpack:Allocating a SIP Network Access Point (NAP) E|Allocating a SIP NAP Configuration v2.10]] |
| − | *[[Toolpack: | + | *[[Toolpack:Allocating a SIP Network Access Point (NAP) D|Allocating a SIP NAP Configuration v2.9]] |
| + | *[[Toolpack:Allocating a SIP Network Access Point (NAP) C|Allocating a SIP NAP Configuration v2.8]] | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-collapsetext="other versions" data-expandtext="Click here for other versions" style="width: 400px;"> | ||
| + | *[[Toolpack:Allocating a SIP Network Access Point (NAP) B|Allocating a SIP NAP Configuration v2.7]] | ||
| + | *[[Toolpack:Allocating a SIP Network Access Point (NAP) B|Allocating a SIP NAP Configuration v2.6]] | ||
| + | *[[Toolpack:Allocating a SIP Network Access Point (NAP) A|Allocating a SIP NAP Configuration v2.5]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | *[[Configuring SIP Registration to SIP Proxy|Configuring SIP Registration to SIP Proxy]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| − | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Session_Initiation_Protocol | + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Session_Initiation_Protocol#Registrar Wikipedia registrar article] |
| + | *[https://andrewjprokop.wordpress.com/2014/05/29/understanding-sip-registration/ Understanding SIP Registration] | ||
| + | *[http://toncar.cz/Tutorials/VoIP/VoIP_Protocols_SIP_Call_Flow.html VoIP Protocols:SIP Call Flow - Toncar.cz] | ||
[[category:Glossary]] | [[category:Glossary]] | ||
[[Category:Revise on Major]] | [[Category:Revise on Major]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:48, 21 November 2019
Contents |
SIP Registrar
A SIP registrar’s role is to accept REGISTER requests with an Address Of Record (URI) and write the associated contact bindings to a location service. The location service is a logical entity and is simply a database that contains a list of AOR to contact address bindings. Very often a registrar functions as a location service. It is also very common for a registrar/location service to be co-located with the proxy server for the same domain. The example below shows a typical registration transaction.
Tmedia supports two modes for SIP Registration:
- The Tmedia forwards per-user registration requests from users
- The Tmedia registers itself to the SIP Proxy (per SIP NAP, as explained below in current page)
Registration per SIP NAP
The Tmedia supports to register a SIP NAP to a SIP proxy. Registration, can be used, for example, to authenticate the Tmedia Gateway IP address to a SIP provider proxy or SBC and allow the SIP traffic from the Tmedia to that SIP provider.
- Registration is when Tmedia sends a SIP REGISTER to a Registrar, and gets a response which could be accepted (200 OK) or refused (4xx reason code). Upon refusal, the registration is not stopped and is retried after 5 seconds.
- Even if there is no call on the system, Tmedia will send SIP REGISTER
- Sending SIP REGISTER will happen when the option "Register to Proxy?" is selected for a specific SIP NAP
- If you apply a new configuration and the option "Register to Proxy?" is present it will start sending SIP REGISTER
Register with no answer from registrar
If it is not registered already, the Tmedia will send a new SIP REGISTER every 32 + 5 seconds interval until it receive a response from the Registrar
- Over UDP (shown it the message flow bellow), the REGISTER request is retransmitted for 32 seconds before the request transaction timeout, then a new SIP REGISTER is sent after 5 seconds.
- Over TCP, if the SIP registrar does not listen on the TCP port, a new TCP connection is retried every 5 seconds. If the TCP connection is established but no SIP responses returned by the Registrar, the transaction timeout after 32s and then a new SIP REGISTER is sent after 5 seconds.
Register expire negotiation
The REGISTER request negotiate the contact binding expiration by adding "expires=3600" parameter to the contact header. The value is hardcoded to 3600 seconds. If the REGISTER response from the Registrar does not change the "expires" parameter:
- The SIP REGISTER will be "valid" for 3600 seconds
- Tmedia will send a new REGISTER (to refresh the registration) after half of the minimum registration negotiated, general use will be at 1800 seconds (3600/2)
The Registrar can change the "expires" contact parameter or the Expires header as shown in the two example below to negotiate a value different from 3600 seconds.
Negotiation uses case 1: contact expires header
In the example below, the Registrar changes the "expires" contact parameter.
Negotiation uses case 2: no contact expires parameter; Expires header
In the example below, the Registrar removes the "expires" contact parameter and set the Expires header.
Register Authentication
- If Authentication is required, the Registrar returns a 401 Unauthorized response with a WWW-Authenticate header
- The WWW-Authenticate header contains nonce to encrypt user’s communications password, user then sends a second REGISTER containing an Authorization header with the user's encrypted password
Configuration
- Allocating a SIP NAP Configuration v3.0
- Allocating a SIP NAP Configuration v2.10
- Allocating a SIP NAP Configuration v2.9
- Allocating a SIP NAP Configuration v2.8