Toolpack:Configuring Vlan SBC A
From TBwiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→List of Parameters: Added parameters) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Configuring a VLAN}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Configuring a VLAN}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |rowspan="2"|This article applies to: | ||
| + | |'''Product''' | ||
| + | |'''Version''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |SBC | ||
| + | |3.1 | ||
| + | |} | ||
After you create a virtual port, you must create a new VLAN. | After you create a virtual port, you must create a new VLAN. | ||
Latest revision as of 08:13, 15 December 2020
| This article applies to: | Product | Version |
| SBC | 3.1 |
After you create a virtual port, you must create a new VLAN.
To configure a VLAN
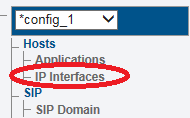
1. Select IP Interfaces from the navigation panel
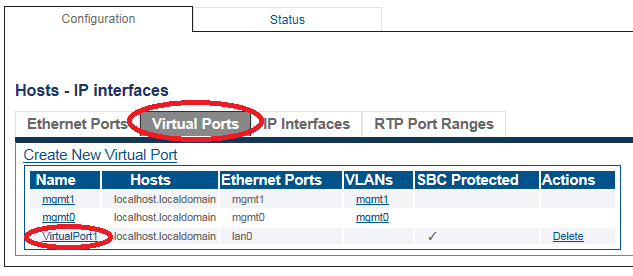
2. Click the Virtual Ports tab.
- Select a Virtual Port
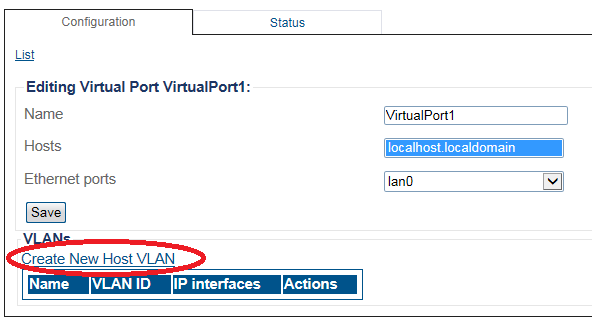
3. Create a VLAN that uses this virtual port
- Click Create new Host VLAN
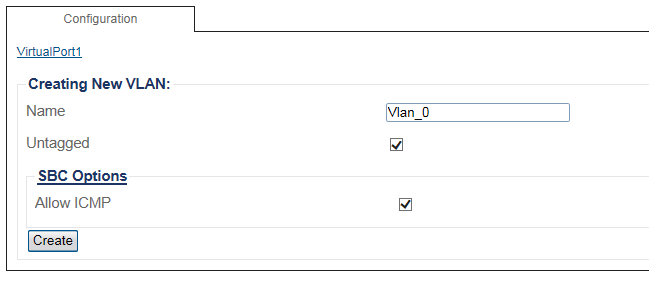
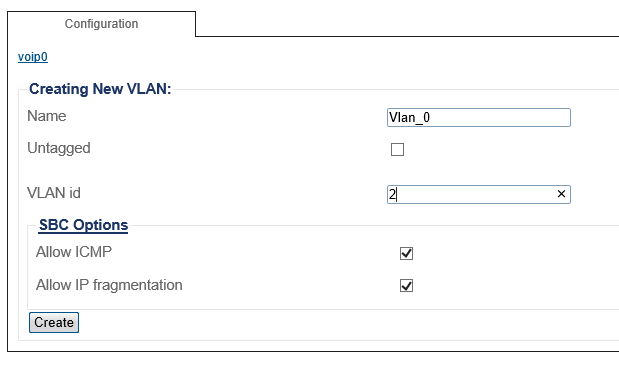
4. Configure the new VLAN
Important Note
Vlans can be configured on the SBC in these cases:
- Baremetal installation
- VMware installation with Passthrough or SR-IOV network interfaces
- VMware installation with a network interface using vlan ID 4095
Vlans should not be configured on the SBC in this case:
- VMware installation with network interfaces using vlans from 1 to 4094
In this case, all interfaces on the SBC should be configured as untagged. Vlans are configured in the VMware port Groups.
Please check here: How to add VMware Network Interfaces
If VLANs must be configured, follow these steps:
- Enter a name for the VLAN
- If the port is to be used untagged, make sure Untagged is checked.
- If the port is to be used with a 802.1Q tag, uncheck Untagged and enter a VLAN ID.
- Click Create
OR