Redundancy & High Availability:Network
(fix link and more detail regarding TMS network) |
(Added info on control ethernet link.) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Network Redundancy == | == Network Redundancy == | ||
| − | + | TelcoBridges recommends the use of 2 Gigabytes Ethernet Switches for a [[Tmedia]] system. | |
| − | + | ||
== VoIP Network == | == VoIP Network == | ||
| Line 36: | Line 35: | ||
[[Image:Ha_Control_Network_Fail.png|TMG7800 Control Network With Network Failure]] | [[Image:Ha_Control_Network_Fail.png|TMG7800 Control Network With Network Failure]] | ||
| + | The control network requires a maximum of 100Mbps and needs to support Broadcast, ARP and ICMPs. | ||
== TMS Network == | == TMS Network == | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
[[Image:Ha_TMS_Network_With_TMG7800-TMS_Failure.png|TMG7800 TMS Network With TMG7800-TMS With Failure]] | [[Image:Ha_TMS_Network_With_TMG7800-TMS_Failure.png|TMG7800 TMS Network With TMG7800-TMS With Failure]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Tmedia_High_Availability|Networking]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:57, 12 August 2016
Networking is a critical section of the system that is sometimes overlooked. An adequate network will avoid problems like congestion or disconnection.
Contents |
Network Redundancy
TelcoBridges recommends the use of 2 Gigabytes Ethernet Switches for a Tmedia system.
VoIP Network
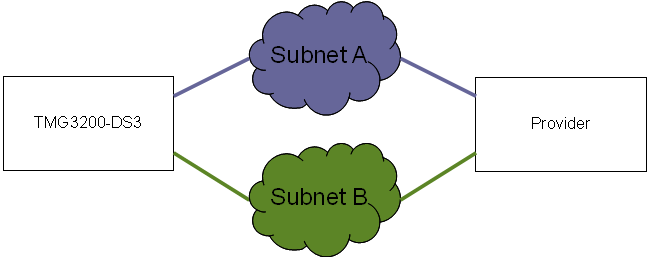
The VoIP network are secured interfaces that are use to send signaling and data packets over Ip networks (i.e. Sip, Sigtran, RTP). They are considered secured because it is not possible to control the Tmedia through those interfaces. TelcoBridges provides 2 VoIP ports on all its VoIP Gateway models.
A different subnet is required for each VoIP interface. The obvious use of the 2 VoIP ports is to connect one port with a private network and the other to the public network. A second application of the 2 VoIP ports are to connect to your providers using 2 different networks.
Here is an example of VoIP network redundancy with a TMG3200
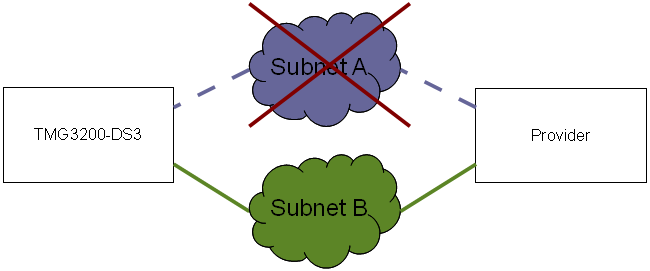
If one of the network is down (because of a switch or cable malfunction), the other network can still reach the providers as seen in the next example
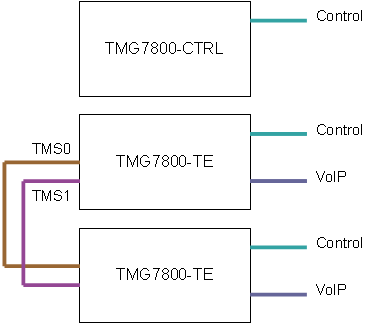
Control Network
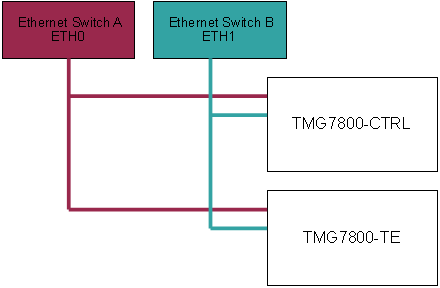
The Control network is only available for the TMG7800 model. The control network allows the TMG-CONTROL to manage the TMG7800 Telecom units. Each TMG7800 units contains 2 control network interfaces labeled ETH0 and ETH1 respectively. The control network should be on private subnets to avoid lost of packets between the TMG7800 units. Which is why TelcoBridges recommends the use of 2 Ethernet switches one for interfaces.
Here is an example of the TMG7800 control network.
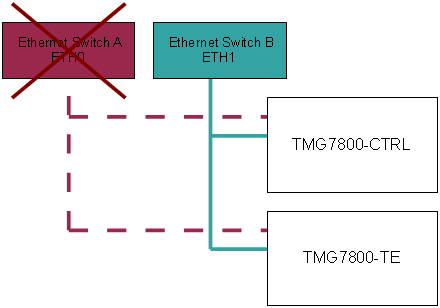
As shown in the next example, the system remains operational even if there is a network failure
The control network requires a maximum of 100Mbps and needs to support Broadcast, ARP and ICMPs.
TMS Network
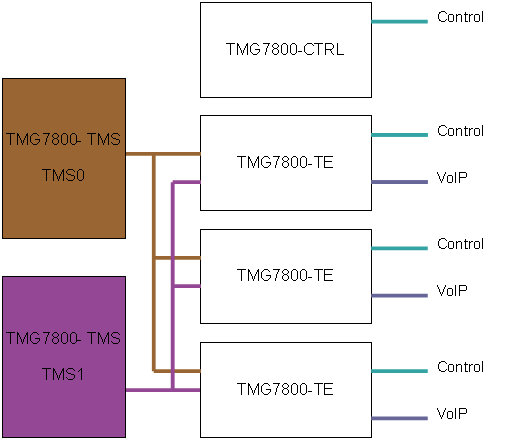
The TMS network is only available for the TMG7800 model. It allows a TMG7800 system to bridge call legs between TMG7800 Telecom Units. It is possible to connect 2 TMG7800 Telecom Units together using RJ45 shielded CAT7 Ethernet cross-over cables. For more than 2 TMG7800 Telecom Units, the TMG7800 system requires a TMG7800-TMS. Each TMG7800 Telecom Units are supplied with 2 TMS interfaces.
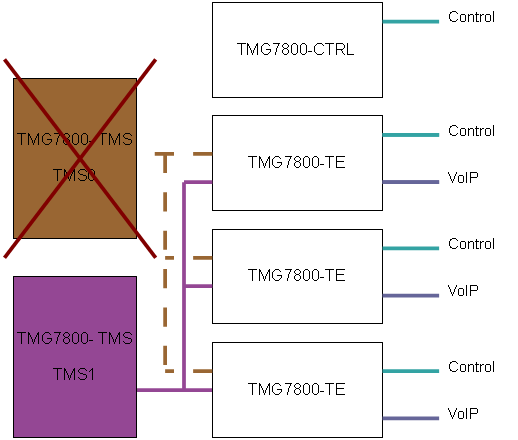
TelcoBridges recommends to always connect both TMS network ports to protect against failure.
Redundant TMS network connection with 2 TMG7800 Telecom units
Redundant TMG7800-TMS for system larger than 2 TMG7800 Telecom units
Even if one of the TMG7800-TMS fails, the TMG7800 system can still have a connection between its units as shown in the next example