Symmetric NAT Traversal
From TBwiki
(Difference between revisions)
Clod Patry (Talk | contribs) (adding active NAT) |
Clod Patry (Talk | contribs) (remove the limitation of not being active) |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Important Reminders == | == Important Reminders == | ||
* All devices in the path must support symmetric RTP/RTCP: RFC 4961 | * All devices in the path must support symmetric RTP/RTCP: RFC 4961 | ||
| − | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 14:11, 3 May 2013
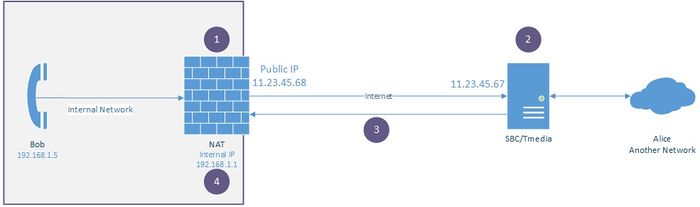
Tmedia supports passive NAT Traversal that addresses the need of peer VoIP endpoint having a private network address. This endpoint device is situated behind a NAT (Network Address Translation) device, e.g. Firewall, while the Tmedia VoIP port has a public IP address. For the passive mode, TMG detects the received RTP packet's source IP address and port. In response, Tmedia uses this source IP address and port as the packet destination for RTP.
Contents |
TelcoBridges and Passive NAT Traversal
Tmedia supports passive NAT Traversal starting from Tmedia release 2.6.31.
TelcoBridges and Active NAT Traversal
Tmedia supports active NAT Traversal starting from Tmedia release 2.7.
Typical Use Case
Important Reminders
- All devices in the path must support symmetric RTP/RTCP: RFC 4961
Configuration
External Sources
- RFC 4961 Symmetric RTP / RTP Control Protocol (RTCP)