Scriptable Routing Engine
(→Steps) |
(→Steps) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
The Toolpack scriptable routing engine is based on the 1.8.x branch of Ruby. | The Toolpack scriptable routing engine is based on the 1.8.x branch of Ruby. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Script routing overview == | ||
| + | The Scriptable Routing Engine is asked, for every incoming call leg, to take a routing decision which indicates how the outgoing call leg must be created. | ||
| + | The script will match one or multiple routes based on information from the incoming call leg | ||
| + | *calling number | ||
| + | *called number | ||
| + | *NAP | ||
| + | Each route determines NAP to use to make outgoing call, and may modify some of the call parameters: | ||
| + | *calling number | ||
| + | *called number | ||
| + | *nature of address | ||
| + | *numbering plan | ||
| + | *calling presentation | ||
| + | *etc. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Multiple routes can match one incoming call, in which case routes can be sorted using various criterias | ||
| + | *round robin | ||
| + | *least cost | ||
| + | *availability percent | ||
| + | *etc. | ||
| + | |||
| + | An outgoing call will be made based on the first matching route. If this call fails before being alerted (maximum capacity reached, network or protocol error), another outgoing call attempt will be made using the next matching route, if possible (this route retry feature is available starting with version 2.5 of Toolpack software). | ||
== Steps == | == Steps == | ||
Revision as of 08:27, 9 December 2009
Toolpack v2.3 introduces a scriptable routing engine that complements the existing approach to building call routes. This new approach is based on the Ruby programming language, which offers a high-level, natural language-like approach to programming known as scripting. With Ruby, no code compilation is required to use routing scripts; in fact, you write scripts within your web browser. A high-level overview of how to write scripts is available upon request by contacting the TelcoBridges support team.
As part of the initial release, TelcoBridges is providing a number of ready-to-use scripts such as percentage routing, round-robin routing, least-cost routing, SIP trunking, PRI reselling with over-subscription, etc., with additional scripts to be made available as we go forward. This new approach is meant to supplement the current approach to building routes. It should also make it possible for your service provider customers, once properly trained by you, to modify routing tables on their own.
Contents |
Prerequisites
There is no additional software required to use the scriptable routing engine. All necessary software is installed by the Toolpack installer application. While the Ruby language is natural language-like and easily approachable, some understanding of programming or Ruby is required in order to modify existing scripts. The Ruby scripts provided with Toolpack essentially consist of a series of mini scripts or sub-scripts (akin to classes in C++); therefore creating a script from scratch does require more experience. Please see the Ruby site for additional information on Ruby. That site features a helpful tutorial called “Ruby in 20 minutes”. There is also a section called “Ruby from Other Languages” which will help you understand Ruby if your frame of reference is C++, Java, or a scripting language such as Perl, PHP, or Python.
The Toolpack scriptable routing engine is based on the 1.8.x branch of Ruby.
Script routing overview
The Scriptable Routing Engine is asked, for every incoming call leg, to take a routing decision which indicates how the outgoing call leg must be created. The script will match one or multiple routes based on information from the incoming call leg
- calling number
- called number
- NAP
Each route determines NAP to use to make outgoing call, and may modify some of the call parameters:
- calling number
- called number
- nature of address
- numbering plan
- calling presentation
- etc.
Multiple routes can match one incoming call, in which case routes can be sorted using various criterias
- round robin
- least cost
- availability percent
- etc.
An outgoing call will be made based on the first matching route. If this call fails before being alerted (maximum capacity reached, network or protocol error), another outgoing call attempt will be made using the next matching route, if possible (this route retry feature is available starting with version 2.5 of Toolpack software).
Steps
You access the Scriptable Routing Engine via the Toolpack web portal. After logging into the Toolpack web portal with your web browser, do the following steps to either modify or create a script and to then activate it.
- To modify a bundled script or to create a script from scratch, go to Gateway > Routing Scripts in the navigation menu on the left hand side of the web page.
- Select Create New Script to generate a default script. Here you will name your script. There is a checkbox called ‘Create default script files’ that is checked by default. If left checked, it will add the default scripts elements to your script.
- In the Editing NAPS section, you are initially presented with a list of NAPS configured on the system. Via the Create New NAP Column item, you have the ability to add custom fields for the purposes of adding weights or other variables that your scripts should take into account.
- The list of available NAPs is accessed via Global > NAPS.
- In addition to authoring scripts in the web browser, Ruby scripts can be authored in any application that offers text editing functionality. Importing a Ruby script into Toolpack is as simple as copying it from the source application document and paste it in to the editing window of the web browser.
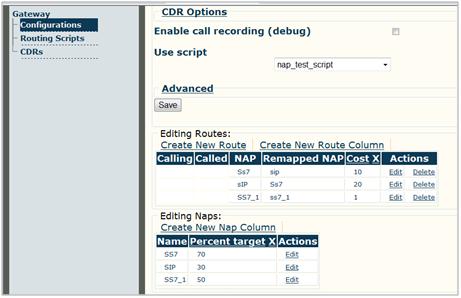
- To assign and activate a script, go to Gateway > Configurations at the bottom of the navigation menu on the left hand side of the web page. If you are already satisfied with your gateway configuration, then click on Edit Configuration to edit your existing gateway configuration. If you want to create a new gateway configuration, click on Create New Configuration. A new window will open. Locate the Use Script sub-menu underneath the Use script section. (See Figure 1). You then click on the pop-up menu and choose the script you want.
- The list of available scripts is determined via the Routing Scripts menu item we saw in the previous bullet.
- Available scripts:
- base_routing
- simple_routing
- simple_least_cost_routing
- least_cost_routing
- simple_routing_selector
- percentage_routing
- asr_routing
- noa_npi_remap_routing_example
Figure 1: Use Script sub-menu
- Once you have selected a script, you need to create routes and network access points (NAPs).
- The Editing Routes section is where you create new routes. In addition to the standard route parameters, you can add new custom parameters as well. These parameters and their values can be accessed in the scripts.
- The Editing Naps section is where you manage NAPs. In addition to the standard NAP parameters, you can add new custom parameters as well. These parameters and their values can be accessed in the scripts.
- This is used to add NAP-specific parameters to the routing scripts.
- The list of NAPs is always populated with the NAPs of your current configurations.
- In order to activate a new script or a modified script, you must force a reload of the gateway’s configuration.
- If you have created a new gateway configuration, you need to change the current configuration of the gateway instance. This can be done by accessing the Instance menu, editing the gateway instance and changing its configuration to your new one. If you have modified an existing gateway configuration, you do need to change anything. In both cases however, you need to activate the configuration in Global > Systems. There you select the system to which you want to apply the configuration, clicking Edit besides its name. In the new page that opens, click Activate in the Active Configuration section.
Tutorial guide
To learn how to use the Scriptable Routing Engine, click the following link to go to the Script Routing Tutorial.
Mini development guide
To learn about the parameters available in for each object go read the Script Routing Mini Development Guide.
Testing this feature
To test this feature, you will want to modify some of the provided scripts by changing variables such as route costing or NAP targets.
Known issues
The following are known issues with the Scriptable Routing Engine as of version 2.3:
- Scripts (including script sub-components provided by TelcoBridges) are not updated when Toolpack is upgraded to new version (for example, to the release version of v2.3.0, v2.3.1, etc.). This means that if there is an update (bug fix) of the basic script, you will need to manually update any existing scripts.
- If you are using dynamic fields (using the Creating New Route Column or the Create New Nap Column option) with routing scripts and you plan to use NAP names, those NAP names need to be all capital letters (i.e.: not just the first letter needs to be capitalized.)