Enabling Local NAT Traversal A
From TBwiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Applies to version: v2.7.) |
(→Applies to version: v2.7.) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
1- Select '''NATs''' from the navigation panel. | 1- Select '''NATs''' from the navigation panel. | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Sip_D_0.png]] |
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
Once the NAT configuration is completed, it must be associated with a NAP. | Once the NAT configuration is completed, it must be associated with a NAP. | ||
| − | 3- Select ''' | + | 3- Select '''NAPs''' from the navigation panel |
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Sip_C_0.png]] |
Latest revision as of 13:49, 12 July 2013
Applies to version: v2.7.
To enable Local NAT Traversal:
1- Select NATs from the navigation panel.
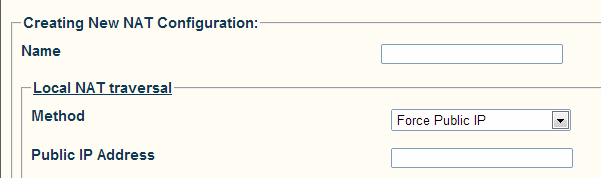
2- Click Create New Configuration
- Enter a meaningful name.
- Choose a Local Method.
- If necessary, provide an extra parameter.
- Click Create
Once the NAT configuration is completed, it must be associated with a NAP.
3- Select NAPs from the navigation panel
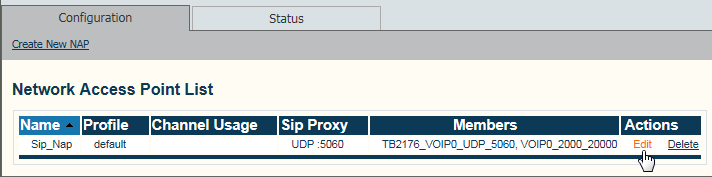
4- Select a SIP NAP from the Network Access Point list
- Click Edit
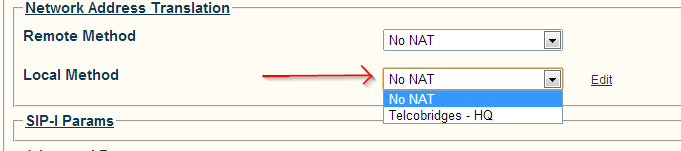
5- In the Network Address Translation section:
- Choose the proper Local Method. The select box will contain the same name as the Local NAT configuration, that you provided in step #2.
- Click Save
The following describes the 2 Local NAT Traversal Methods:
No NAT
This method is used if you are not behind a NAT. This is the default value.
Force Public IP
This method will set some of the SIP Headers and SDP fields with the IP address that you set.