Enabling Remote NAT Traversal B
(2.8 article) |
|||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
2- Select a SIP NAP from the '''Network Access Point List''' | 2- Select a SIP NAP from the '''Network Access Point List''' | ||
| − | |||
[[Image:EnableRemoteNatTraversal_1.png]] | [[Image:EnableRemoteNatTraversal_1.png]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:56, 12 November 2014
Applies to version: v2.8.
To enable Remote NAT Traversal:
1- Select NAPs from the navigation panel
2- Select a SIP NAP from the Network Access Point List
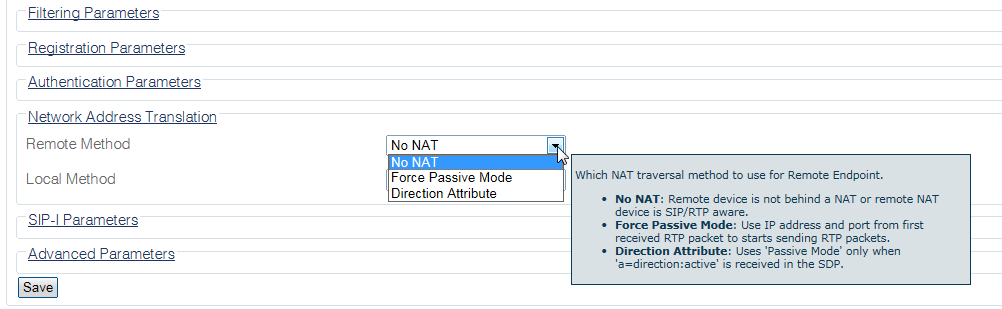
3- In the Network Address Translation section:
- Choose the desired "remote method".
- Click Save
The 3 Remote NAT Traversal Methods are described as follows:
No NAT
The local endpoint is NOT behind a NAT. This means, your local endpoint has a Public IP address, which is globally routable on the Internet. For further information, refer to http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Private_network.
Force Passive Mode
The TMG will NOT send any RTP packets and will wait for the first RTP packet. The remote endpoint will send the first RTP packet. It will ignore the IP address/port sent in the SDP (in the SIP '200 OK' message)and use the IP address/port from where it received the RTP packet.
Note: If the remote endpoint is also set as passive, this method will not work because both sides will wait for the first incoming RTP packet.
Parse Direction Attribute
The TMG will look in the SDP to find an attribute direction:active. If it finds this attribute, the TMG will act exactly as the “Force Passive Mode” method. In fact, this a dynamic way to enable the “Force Passive Mode”.