SS7
(added variants info) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Image:Ss7-protocol-stack.jpg|thumb|300px|Diagram of the SS7 stack]] | ||
SS7 is a signaling protocol which is used to set up and tear down phone calls. It also provides support for such functionality as local number portability, Short Messaging Service (SMS), prepaid billing and number translation. | SS7 is a signaling protocol which is used to set up and tear down phone calls. It also provides support for such functionality as local number portability, Short Messaging Service (SMS), prepaid billing and number translation. | ||
The configuration of SS7 requires that the physical layer, through to the transport layer, and up to the application layer be configured. SS7 configuration involves configuring values for [[MTP2 Layer]], [[MTP3 Layer]], and [[ISUP]]. | The configuration of SS7 requires that the physical layer, through to the transport layer, and up to the application layer be configured. SS7 configuration involves configuring values for [[MTP2 Layer]], [[MTP3 Layer]], and [[ISUP]]. | ||
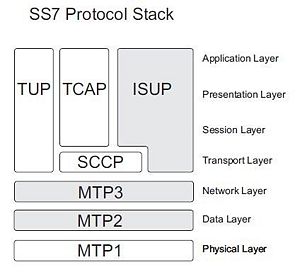
| − | A conceptual illustration of the SS7 protocol stack is shown | + | A conceptual illustration of the SS7 protocol stack is shown on the right. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| Line 13: | Line 11: | ||
TelcoBridges provides SS7 support with all of its media gateway, VAS development platform and monitoring devices. SS7 functionality is licensed separately and can be provided at initial purchase or added later on via a software [[Add/Change_Licenses|license upgrade]]. | TelcoBridges provides SS7 support with all of its media gateway, VAS development platform and monitoring devices. SS7 functionality is licensed separately and can be provided at initial purchase or added later on via a software [[Add/Change_Licenses|license upgrade]]. | ||
| − | SS7 signaling is configured once for the entire [[Tmedia]] or [[Tdev]] system. Any one | + | SS7 signaling is configured once for the entire [[Tmedia]] or [[Tdev]] system. Any one Tdev unit is capable of running the entire SS7 signaling stack for all the Tdev units in a system. |
| − | + | ||
Systems developed using TelcoBridges hardware can support up to a maximum of 64 point codes. It is worth noting that a single pointcode can be used for 2 or more devices configured as a single system. | Systems developed using TelcoBridges hardware can support up to a maximum of 64 point codes. It is worth noting that a single pointcode can be used for 2 or more devices configured as a single system. | ||
[[High Availability|High availability]] (HA) has been designed into the architecture of the Tmedia product such that the failure of an SS7 stack on one Tmedia unit will be taken over by the SS7 stack of another Tmedia unit. | [[High Availability|High availability]] (HA) has been designed into the architecture of the Tmedia product such that the failure of an SS7 stack on one Tmedia unit will be taken over by the SS7 stack of another Tmedia unit. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Supported SS7 variants === | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''MTP1 and MTP2''' | ||
| + | *56, 64, n x 64 kbps low-speed links (LSL) | ||
| + | *1.5 and 2 Mbps high-speed links (HSL) | ||
| + | *Supports dynamic link configuration | ||
| + | *Supported variants | ||
| + | **ITU-T, Q.701, Q.703 | ||
| + | **ANSI T1.111.3 | ||
| + | **JT Q.703 (TTC, Japan) | ||
| + | **NTT Q.703 (NTT, Japan) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''MTP3''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Up to 64 OPCs per system | ||
| + | *Up to 64 linksets per system | ||
| + | *Point code sharing by multiple devices with external Toolpack control | ||
| + | *Supported variants | ||
| + | **ANSI (used for ANSI88 and ANSI92) | ||
| + | **ANSI96 (used for ANSI96 and Telcordia) | ||
| + | **ITU (used for ITU88, ITU92, ITU97, Q767, Singapore and ETSI) | ||
| + | **China, GF001-9001 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''ISUP''' | ||
| + | *Control of up to 30,000 CICs per system | ||
| + | *Supported variants | ||
| + | **ANSI 88, T1.113 (1998) | ||
| + | **ANSI 92, T1.113 (1992) | ||
| + | **ANSI 95, T1.113.1 – T1.113.4 (1995) | ||
| + | **ITU 92, Q.761 – Q.764 (1993) | ||
| + | **ITU 97, Q.761 – Q.764 (1997), Q.763 Addendum 1 (05/1998), Q.765 ISUP ASE module (05/1998) | ||
| + | **Q.767, ITU 1991 | ||
| + | **Singapore Telecom, Common Channel Signalling System N.7, Singapore Telecom, 1988 | ||
| + | **Telcordia 97, GR-317, GR-394 | ||
| + | **ISUP UK | ||
| + | **ETSI (V2 and V3): ETS 200 356, ETS 300 356 | ||
| + | **ISUP China | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
== Related actions == | == Related actions == | ||
Revision as of 10:42, 21 July 2009
SS7 is a signaling protocol which is used to set up and tear down phone calls. It also provides support for such functionality as local number portability, Short Messaging Service (SMS), prepaid billing and number translation.
The configuration of SS7 requires that the physical layer, through to the transport layer, and up to the application layer be configured. SS7 configuration involves configuring values for MTP2 Layer, MTP3 Layer, and ISUP.
A conceptual illustration of the SS7 protocol stack is shown on the right.
Contents |
TelcoBridges and SS7
TelcoBridges provides SS7 support with all of its media gateway, VAS development platform and monitoring devices. SS7 functionality is licensed separately and can be provided at initial purchase or added later on via a software license upgrade.
SS7 signaling is configured once for the entire Tmedia or Tdev system. Any one Tdev unit is capable of running the entire SS7 signaling stack for all the Tdev units in a system.
Systems developed using TelcoBridges hardware can support up to a maximum of 64 point codes. It is worth noting that a single pointcode can be used for 2 or more devices configured as a single system.
High availability (HA) has been designed into the architecture of the Tmedia product such that the failure of an SS7 stack on one Tmedia unit will be taken over by the SS7 stack of another Tmedia unit.
Supported SS7 variants
MTP1 and MTP2
- 56, 64, n x 64 kbps low-speed links (LSL)
- 1.5 and 2 Mbps high-speed links (HSL)
- Supports dynamic link configuration
- Supported variants
- ITU-T, Q.701, Q.703
- ANSI T1.111.3
- JT Q.703 (TTC, Japan)
- NTT Q.703 (NTT, Japan)
MTP3
- Up to 64 OPCs per system
- Up to 64 linksets per system
- Point code sharing by multiple devices with external Toolpack control
- Supported variants
- ANSI (used for ANSI88 and ANSI92)
- ANSI96 (used for ANSI96 and Telcordia)
- ITU (used for ITU88, ITU92, ITU97, Q767, Singapore and ETSI)
- China, GF001-9001
ISUP
- Control of up to 30,000 CICs per system
- Supported variants
- ANSI 88, T1.113 (1998)
- ANSI 92, T1.113 (1992)
- ANSI 95, T1.113.1 – T1.113.4 (1995)
- ITU 92, Q.761 – Q.764 (1993)
- ITU 97, Q.761 – Q.764 (1997), Q.763 Addendum 1 (05/1998), Q.765 ISUP ASE module (05/1998)
- Q.767, ITU 1991
- Singapore Telecom, Common Channel Signalling System N.7, Singapore Telecom, 1988
- Telcordia 97, GR-317, GR-394
- ISUP UK
- ETSI (V2 and V3): ETS 200 356, ETS 300 356
- ISUP China
Related actions