Toolpack:Configuring Virtual Port C
From TBwiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→To configure a virtual port) |
(→Applies to version(s): v2.10) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | === '''''Applies to version(s): v2.10''''' === | + | === '''''Applies to version(s): v2.10, v3.0''''' === |
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Configuring a Virtual Port}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Configuring a Virtual Port}} | ||
One or more virtual ports can be created to manage IP traffic. | One or more virtual ports can be created to manage IP traffic. | ||
| − | <br> | + | <br> |
== To configure a virtual port == | == To configure a virtual port == | ||
Revision as of 13:05, 23 October 2017
Applies to version(s): v2.10, v3.0
One or more virtual ports can be created to manage IP traffic.
To configure a virtual port
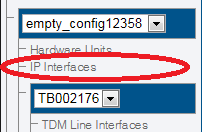
1. Select IP Interfaces from the navigation panel
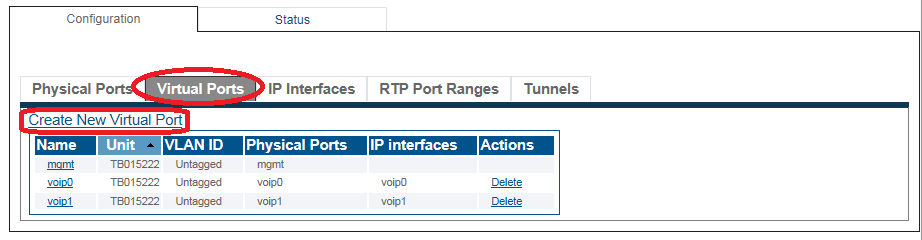
2. Click the Virtual Ports tab.
- Click Create New Virtual Port
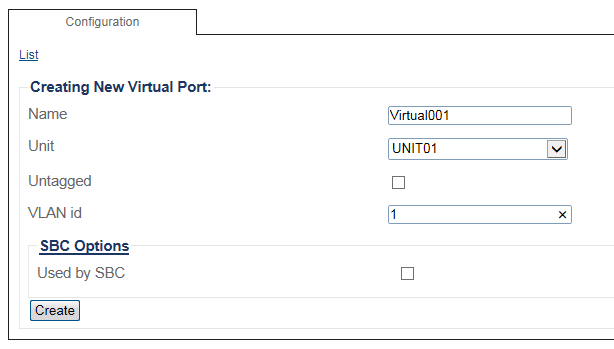
3. Configure the virtual port.
- Enter a name for the virtual port
- Select the hardware device to which the virtual port is assinged
- Enter a VLAN ID
- Click Create
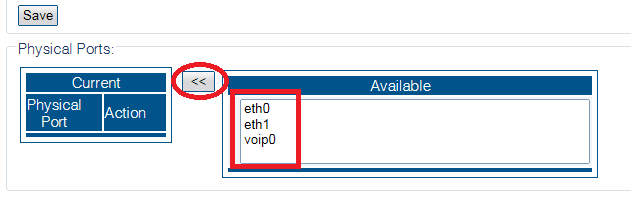
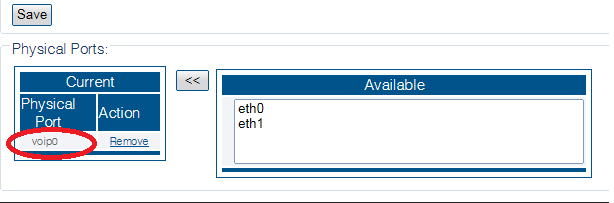
4. From the Available ports window, select a physical port to which the virtual port is assigned. Note that this window is scrollable.
The selected port is displayed in the current physical ports window.
Path
/configurations/@[configuration_name]/hardware_units/@[hardware_name]/virtual_ports/@[port_name]
Parameters (text)
/configurations/@[configuration_name]/hardware_units/@[hardware_name]/virtual_ports/@[port_name] ethernet_ports = [ "@[port_name]" ] name = "@[port_name]" untagged = true vid = 0
Parameters (json)
{
"ethernet_ports" : [
"@[port_name]"
],
"name" : "@[port_name]",
"untagged" : true,
"vid" : 0
}