Symmetric NAT Traversal
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Typical Use-Case == | == Typical Use-Case == | ||
A Network Address Translation (NAT) has many functions such as: firewall, hiding the client IP. Usually, a NAT limits the number of "opened" IPs/Ports allowed to communicate with the internal network and ignores all messages addressed to the "closed" IPs/Ports. A typical call can be described as follow: | A Network Address Translation (NAT) has many functions such as: firewall, hiding the client IP. Usually, a NAT limits the number of "opened" IPs/Ports allowed to communicate with the internal network and ignores all messages addressed to the "closed" IPs/Ports. A typical call can be described as follow: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | <br> |
| + | [[File:passive_nat_traversal_use_case.jpg|700px]] | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
== TelcoBridges and Passive NAT Traversal == | == TelcoBridges and Passive NAT Traversal == | ||
Tmedia supports passive NAT Traversal that addresses the need of peer VoIP endpoint having a private network address. This endpoint device is situated behind a NAT device, e.g. Firewall, while the Tmedia VoIP port has a public IP address. For the passive mode, TMG detects the received RTP packet's source IP address and port. In response, Tmedia uses this source IP address and port as the packet destination for RTP. | Tmedia supports passive NAT Traversal that addresses the need of peer VoIP endpoint having a private network address. This endpoint device is situated behind a NAT device, e.g. Firewall, while the Tmedia VoIP port has a public IP address. For the passive mode, TMG detects the received RTP packet's source IP address and port. In response, Tmedia uses this source IP address and port as the packet destination for RTP. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 21: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
== Important Reminders == | == Important Reminders == | ||
Revision as of 14:51, 26 March 2018
Tmedia supports NAT (Network Address Translation) Traversal.
Contents |
Typical Use-Case
A Network Address Translation (NAT) has many functions such as: firewall, hiding the client IP. Usually, a NAT limits the number of "opened" IPs/Ports allowed to communicate with the internal network and ignores all messages addressed to the "closed" IPs/Ports. A typical call can be described as follow:
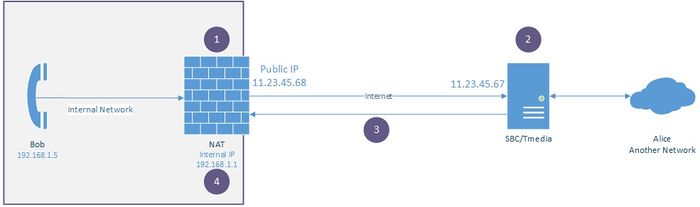
TelcoBridges and Passive NAT Traversal
Tmedia supports passive NAT Traversal that addresses the need of peer VoIP endpoint having a private network address. This endpoint device is situated behind a NAT device, e.g. Firewall, while the Tmedia VoIP port has a public IP address. For the passive mode, TMG detects the received RTP packet's source IP address and port. In response, Tmedia uses this source IP address and port as the packet destination for RTP.
This is also called Remote NAT traversal or far-end NAT traversal.
TelcoBridges and Active NAT Traversal
Active NAT traversal means the TMG endpoint is behind a NAT. The Tmedia unit can advertise a public IP so that the remote device will know where to send the RTP traffic. It can also send the 'a=direction:active' in SIP SDP attribute so that the remote device puts itself in passive mode.
This is also called Local NAT traversal or near-end NAT traversal.
Important Reminders
- All devices in the path must support symmetric RTP/RTCP: RFC 4961
Configuration
- Configure NAT Traversal for version 3.0
- Configure NAT Traversal for version 2.10
- Configure NAT Traversal for version 2.9
- Configure NAT Traversal for version 2.8
- Toolpack v2.7: SIP Advance Features
- Toolpack v2.6: SIP Advance Features
External Sources
- RFC 4961 Symmetric RTP / RTP Control Protocol (RTCP)