TUCL
From TBwiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Features) |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
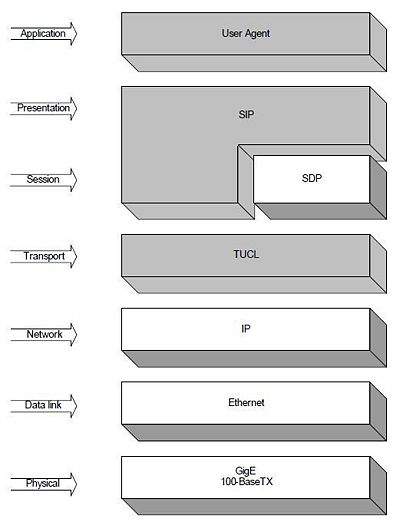
| − | TelcoBridges' [[SIP]] implementation works on top of | + | TelcoBridges' [[SIP]] implementation works on top of several layers, including SIP and TUCL. TUCL stands for TCP/UDP Convergence Layer. TUCL offers TCP/IP and UDP/IP services to TelcoBridges' SIP stack. TUCL virtualizes physical Ethernet interfaces, making them globally accessible within the TelcoBridges' system. |
| − | In the following figure, grey boxes represent entities that need allocation on the TelcoBridges equipment. The TUCL layer is a transport layer used by SIP on our architecture. TUCL presents some advantages over a simple TCP/IP stack | + | In the following figure, grey boxes represent entities that need allocation on the TelcoBridges equipment. The TUCL layer is a transport layer used by SIP on our architecture. TUCL presents some advantages over a simple TCP/IP stack; for instance, it adds tracing facilities to any virtual interface. |
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
[[category:Glossary]] | [[category:Glossary]] | ||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 12:08, 1 May 2018
TelcoBridges' SIP implementation works on top of several layers, including SIP and TUCL. TUCL stands for TCP/UDP Convergence Layer. TUCL offers TCP/IP and UDP/IP services to TelcoBridges' SIP stack. TUCL virtualizes physical Ethernet interfaces, making them globally accessible within the TelcoBridges' system.
In the following figure, grey boxes represent entities that need allocation on the TelcoBridges equipment. The TUCL layer is a transport layer used by SIP on our architecture. TUCL presents some advantages over a simple TCP/IP stack; for instance, it adds tracing facilities to any virtual interface.
Features
TUCL adds the following functionality to SIP: