Sip registration forwarding
(Updating doc (not referring to Topology Hiding)) |
(Added link to SIP registration) |
||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
*[[Toolpack:Creating_a_SIP_Domain_SBC_A|3.0 Creating a SIP Domain]] | *[[Toolpack:Creating_a_SIP_Domain_SBC_A|3.0 Creating a SIP Domain]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | [[SIP_Registration|SIP Registration]] | ||
Revision as of 10:20, 21 September 2018
Contents |
SIP Registration forwarding overview
FreeSBC registration forwarding feature allows to control the registration requests flow between SIP User Agents and registrars.
- It allows adaptation of SIP register messages between SIP User Agents and registrars.
- It allows adaptation of SIP Subscribe/Publish/Notify forwarding messages between SIP User Agents and registrars.
- It keeps information about SIP User Agent contacts to allow routing of SIP calls base on registration information.
Forwarding Modes
- FreeSBC always modifies the contact URI in SIP register requests to remain on the path between SIP User Agents and registrars.
- FreeSBC supports two different SIP registration forwarding modes (i.e. "Contact Remapping" or "Contact Passthrough").
- The "Contact Passthrough" forwarding mode makes contact username portion of the contact URI in SIP register requests to pass through unchanged.
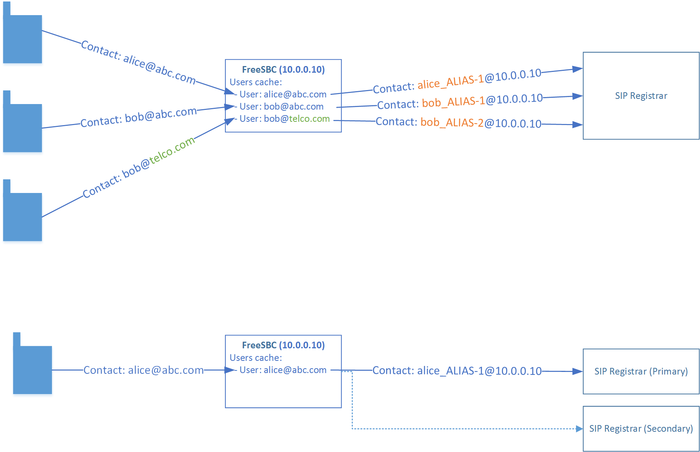
- The "Contact Remapping" forwarding mode modifies contact username portion of the contact URI in SIP register requests and make it unique.
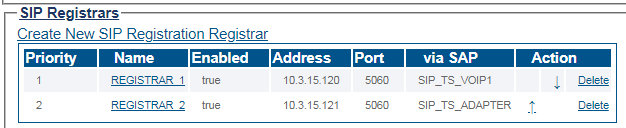
Registrar Selection Mode (registration redundancy)
- FreeSBC supports Active/Standby registrar selection mode. Users's registration requests are forwarded to the available registrar with highest priority.
Protection
- FreeSBC protects the registrar(s) against excessive SIP User Agents register requests using different strategies (i.e. Firewall, Rate Adaptation, SIP Header Manipulation, Etc.).
Contact remapping
When forwarding a SIP Register message from a user to the registrar, FreeSBC will remap the contact to make itself the contact. This way, the Registrar will send response messages through FreeSBC, and thus make sure to "hide" private network topology from users (avoid messages being sent directly from registrar to users).
Because the contact's domain is being remapped, FreeSBC will also remap the contact's user name to make sure there is not user name conflict between two domains that would have the same user name.
NAT traversal
- FreeSBC handles SIP Calls NAT traversal to allow interaction between SIP User Agents from public and private networks.
- FreeSBC detects the actual IP from which users have registered from, so response messages and SIP Invite requests can be forwarded properly, even in case users are unaware that they are behind a NAT
- It supports SIP register requests "Rate Adaptation" between SIP User Agents and registrar.
- Because refreshing requests are not always sent to registrar, "Rate adaptation" feature reduces SIP register requests sent to registrar. The "Rate Adaptation" feature is also useful to keep firewall ports open.
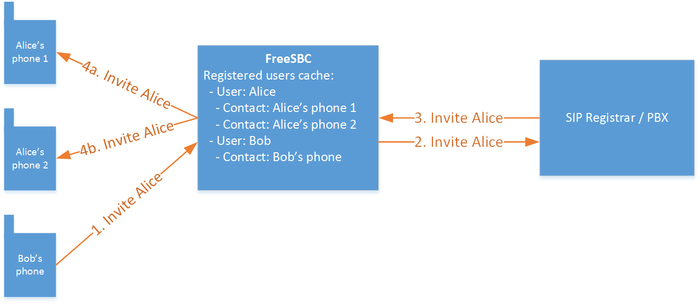
SIP Calls routing per registered user
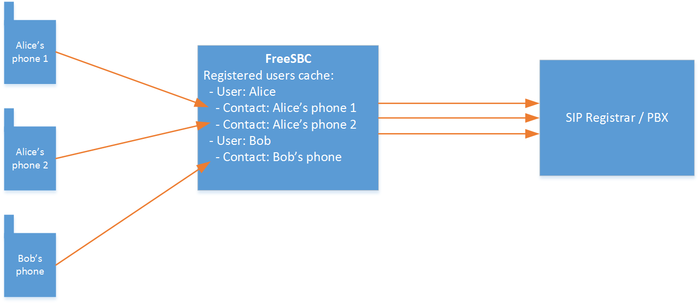
- FreeSBC keeps SIP User Agents contacts information. This information serves on SIP calls routing when a SIP User Agent is trying to reach a registered users. It could be used also to accept calls from registered users only.
Registered users and routing scripts
Registered users can be reached by creating static routes without a specific "outbound NAP". These routes, instead of forwarding calls to a specific NAP, will dynamically choose the outbound NAP by matching the target registered user.
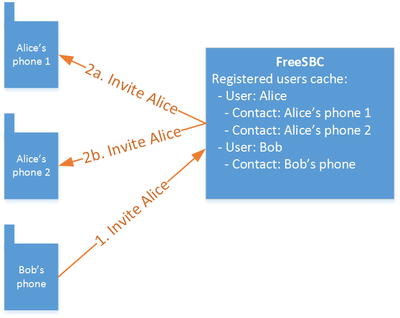
When a user has registered multiple contacts (devices), they will be called one by one in a Route retry manner.
FreeSBC routes can also be organized so calls always go through the Registrar/PBX before being forwarded to the called user.
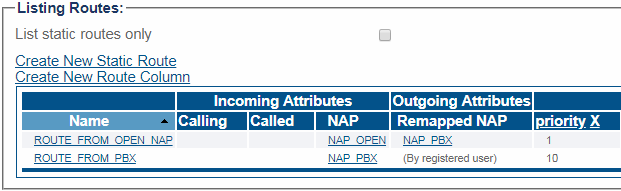
Example:
In this example, there are 2 routes:
- ROUTE_FROM_OPEN_NAP will match all incoming calls received from NAP_OPEN, and forward them to NAP_PBX
- ROUTE_FROM_PBX will match all incoming calls received from NAP_PBX, and forward them by registered user (will forward to whatever NAP the target user has registered from)
Here, if "alice" calls "bob" from NAP_OPEN, the call will be forwarded to the PBX. Then the PBX may route back the call to the SBC, which will then forward to "bob" on NAP_OPEN. In other words, all calls from NAP_OPEN will go through the PBX.
In this example, the routes are exclusive (only one will match for a given incoming call). But there could be multiple matching routes. In this case, routes will be ordered by priority (whether they route by registered user, or to a specific outbound NAP).
Configuration
| FreeSBC |
|---|