FreeSBC:Cloud:Azure Installation A
(→Add inbound security rules) |
(→Instantiate a FreeSBC) |
||
| Line 200: | Line 200: | ||
==== Add inbound security rules ==== | ==== Add inbound security rules ==== | ||
| − | *Select | + | Follow this procedure to add inbound security rules: |
| + | *Log in to the dashboard. | ||
| + | *Select the 'Virtual machines' item from the left menu. | ||
| + | *The 'Virtual machines' list dialog box appears. | ||
| + | *Select the appropriate virtual machine to add inbound security rules. | ||
| + | *The virtual machine overview dialog box appears. | ||
| + | *Select 'Networking' item from the virtual machine 'Settings' section. | ||
| + | *Click the 'Add inbound port rule' button. | ||
| + | |||
==== Advanced Networking ==== | ==== Advanced Networking ==== | ||
Revision as of 12:59, 9 April 2019
WARNING: This page is under construction
This page is intended to give assistance to people launching an instance of FreeSBC on Microsoft Azure infrastructure.
Requirements
Minimal Azure cloud requirements:
- 2 VCPUs
- 4 GB RAM
- Network interface with Advanced Network capability (Mellanox NIC interface)
Following are VM Size suggestions according to performance target in terms of number of sessions:
| Sessions | VM Size | VCPUs | RAM |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Up to 350* |
D2 v2, DS2_v2 |
2 |
7 Gb |
|
350*-1000* |
D4 v3, D4s_v3 |
4 |
16 Gb |
|
1000*-2000* |
D8 v3, D8s_v3 |
8 |
32 Gb |
|
2000*-4000* |
D16 v3, D16s_v3 |
16 |
66 Gb |
*Preliminary estimated values
Getting the Image
Please go to our FreeSBC Download site to get a copy of the latest FreeSBC Image.
Installation on Azure cloud
FreeSBC Azure Image
A virtual machine image is a single file that contains a virtual disk that has a bootable operating system installed on it. Images are used to create virtual machine instances within the cloud.
You will need to upload the latest FreeSBC image into your Microsoft Azure account before you can launch a virtual machine instance running the FreeSBC software.
Get a storage account
You'll need a blob container in your storage account in Azure to store the uploaded FreeSBC VM image. You can either use an existing storage account or create a new one. The storage account is linked to a resource group which contains location information. Note that the storage account location must be at the same location where you'll be creating the VM.
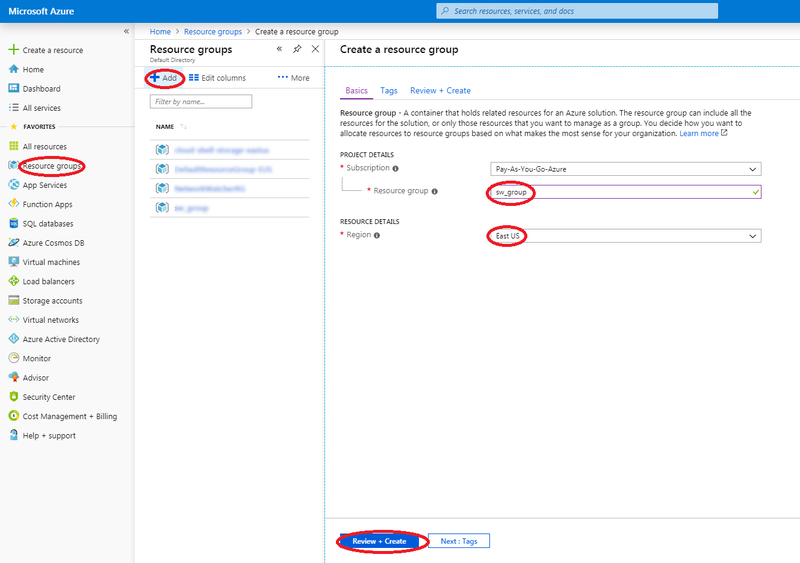
Create resource group
If you need to create a storage account to upload VM image then you will need a resource group matching the location where you'll be creating the VM. Here is a procedure to create a resource group if required to do so:
- Log in to the dashboard.
- Select 'Resource groups' item from the left menu.
- From 'Resource groups' top menu, click 'Add' item.
- The 'Create a resource group' dialog box appears.
- Provide a name to this resource group.
- Select the appropriate resource group location (where you'll be creating the VM).
- Click the 'Review + Create' button
- Wait for completion of resource group creation before proceeding with following steps.
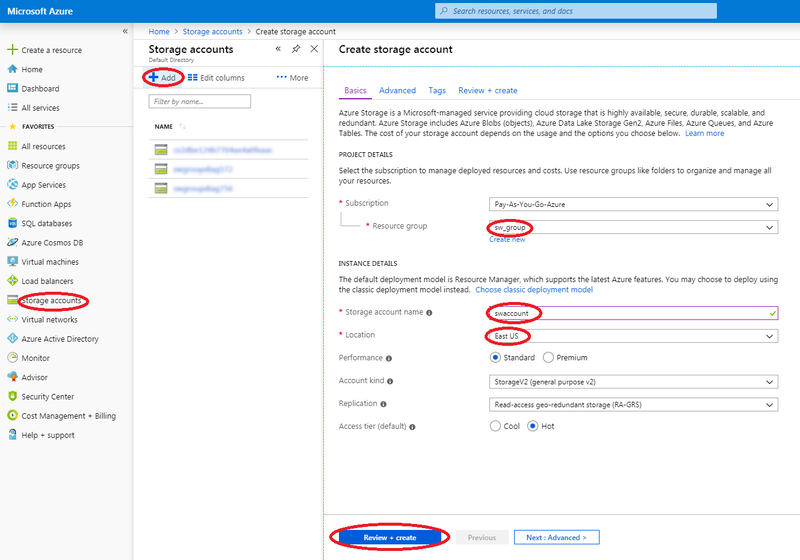
Create storage account
Here is a procedure to create a storage account if required to do so:
- Log in to the dashboard.
- Select 'Storage accounts' item from the left menu.
- From 'Storage accounts' top menu, click 'Add' item.
- The 'Create a storage account' dialog box appears.
- Select the appropriate resource group.
- Provide a name to this storage account.
- Select the appropriate storage account location (where you'll be creating the VM).
- For the other parameters, consult https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure for more details.
- Click the 'Review + Create' button
- Wait for completion of storage account creation before proceeding with following steps.
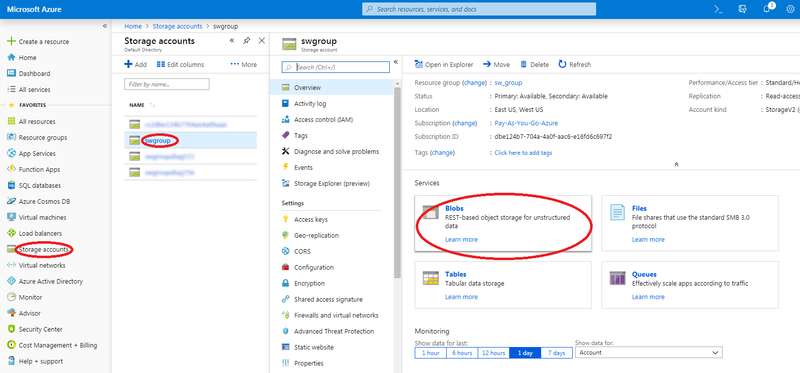
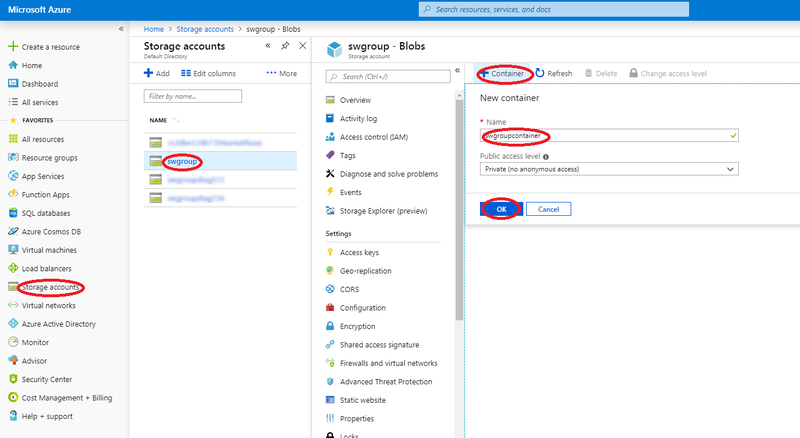
Create storage blob container
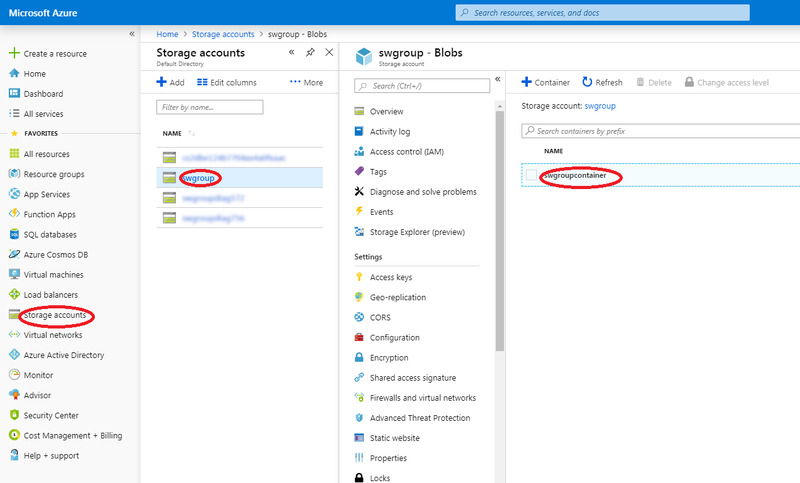
Here is a procedure to create a blob container in storage account if required to do so:
- Log in to the dashboard.
- Select 'Storage accounts' item from the left menu.
- Click on storage account item to add blob container.
- Click on the Blob Services button
- From 'Blobs' top menu, click 'Container' item.
- The 'Blob container' dialog box appears.
- Provide a name to this blob container.
- For the other parameters, consult https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure for more details.
- Click the 'Ok' button
- Wait for completion of storage blob container before proceeding with following steps.
Upload a Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) Image
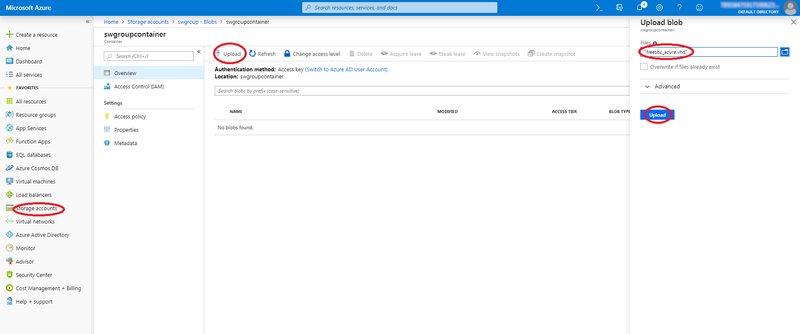
Follow this procedure to upload the FreeSBC image to a storage blob container:
- Before being able to upload the FreeSbc image in the storage blob container, it is required to uncompress (tag.gz) the FreeSBC image locally on your PC. You will require at least 40 GB of free space to uncompress the image.
- Log in to the dashboard.
- Select the 'Storage accounts' item from the left menu.
- Select the appropriate 'storage account' then 'Blobs' container.
- From the 'Blobs' container top menu, Click 'Upload' menu item.
- The 'Upload blob' dialog box appears.
- Select the Virtual Hard Disk image (freesbc_azure.vhd) to upload from your local disk image location.
- Click 'Upload' button
- Wait until upload completion before proceeding with following steps.
Create a VM Image from the FreeSBC storage blob
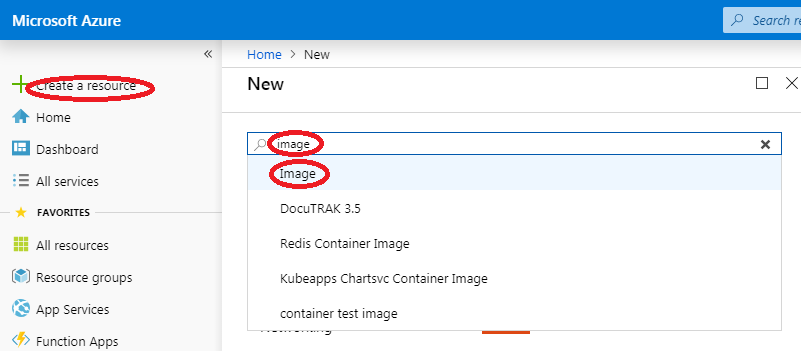
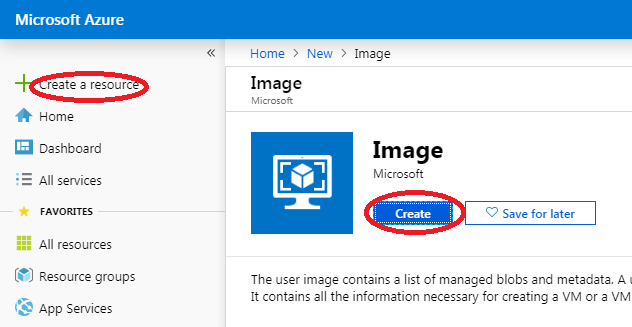
Follow this procedure to create a VM image from a storage blob:
- Log in to the dashboard.
- Select the 'Create a resource' item from the left menu.
- The 'Create resource' dialog box appears.
- Type 'image' in the search text box.
- A list of suggested items appears
- Click 'image' item
- The 'Create image' dialog box appears.
- Click 'Create' button.
- Provide an image name
- Select the appropriate resource group.
- Select the appropriate location.
- Click on 'Linux' button for the OS type.
- Browse through storage accounts to select the FreeSBC blob.
- Click 'Select' button to complete FreeSBC blob selection.
- For the other parameters, consult https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure for more details.
- Click 'Create' button.
- Wait until create completion before proceeding with following steps.
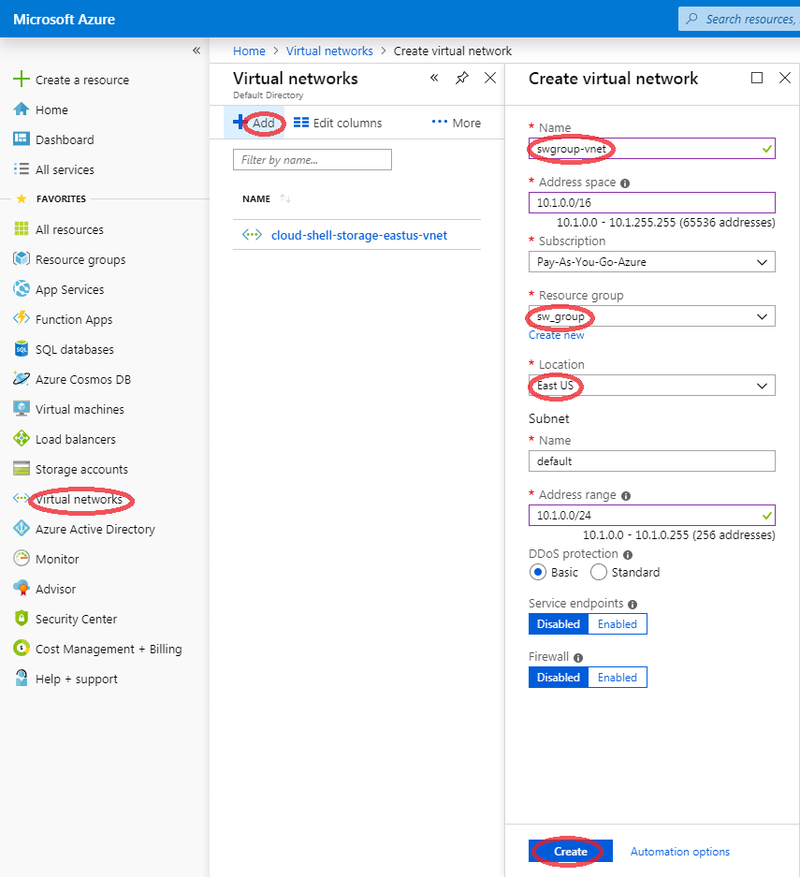
Create a Virtual Network
Follow this procedure to create a Virtual Network if not already available:
- Log in to the dashboard.
- Select the 'Virtual networks' item from the left menu.
- The 'Virtual networks' dialog box appears.
- From 'Virtual networks' top menu, click 'Add' item.
- The 'Create a virtual network' dialog box appears.
- Provide a virtual network name.
- Provide virtual network's address range in CIDR notation.
- Select appropriate resource group.
- Select appropriate location.
- Provide subnet name and address range.
- For the other parameters, consult https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure for more details.
- Click 'Create' button.
- Wait until create completion before proceeding with following steps.
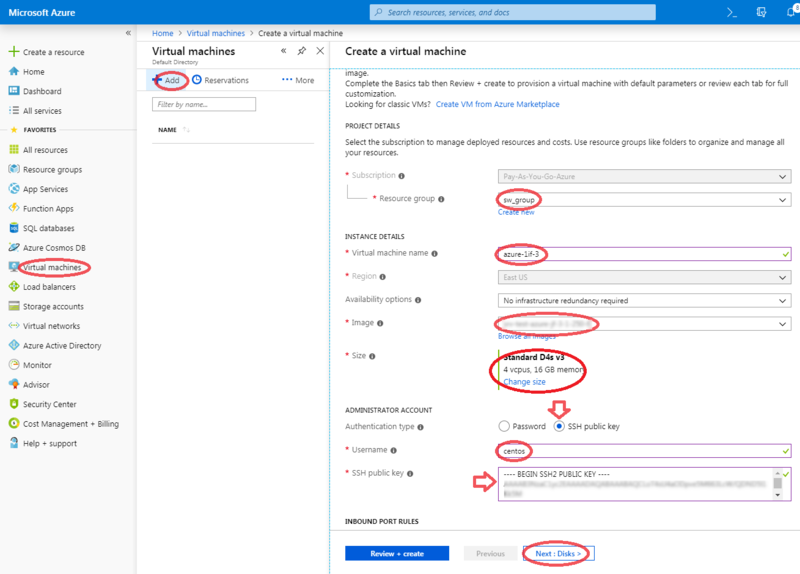
Instantiate a FreeSBC
Follow this procedure to create a FreeSBC instance:
- Log in to the dashboard.
- Select the 'Virtual machines' item from the left menu.
- The 'Create a virtual machine' dialog box appears.
- Select the appropriate resource group.
- Provide a virtual machine name.
- Select the appropriate Region (where you'll be creating the VM).
- Browse VM images to select appropriate FreeSBC VM image.
- Select VM size according to expected performace.
- Select 'SSH public key' option as Authentification type
- Type 'centos' as SSH Authentification Username.
- Provide a SSH public key as SSH Authentification.
- Click bottom 'Next:Disk>' button
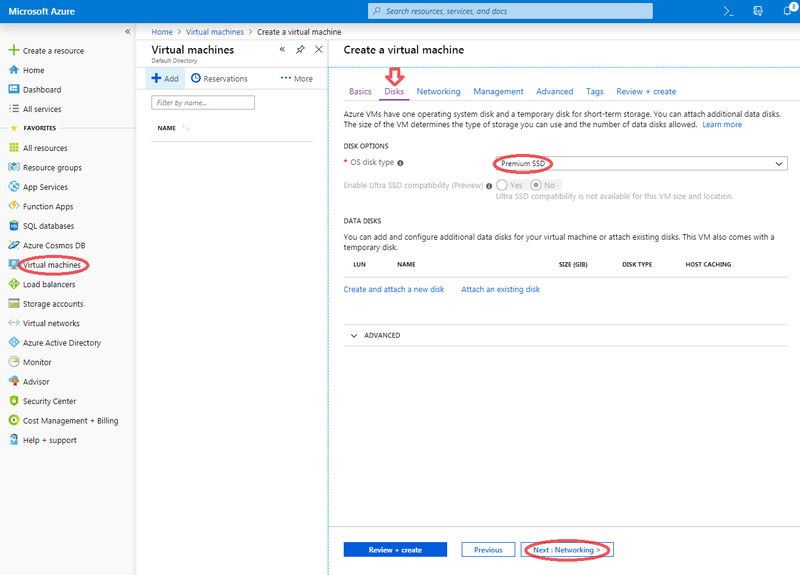
- The Disks dialog box appears.
- Select the appropriate 'OS disk type' to support your workload or scenario.
- Click bottom 'Next:Networking>' button
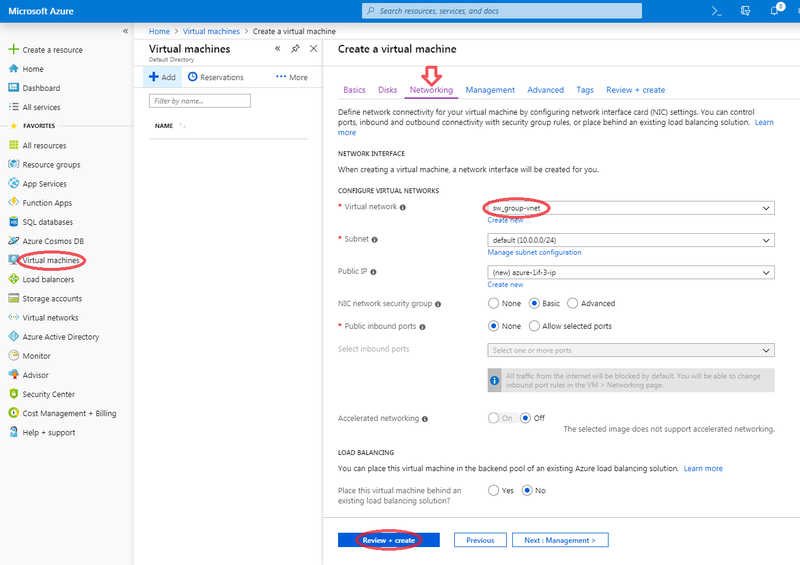
- Select the appropriate Virtual network
- For the other parameters of this page and following pages, consult https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure for more details.
- Click bottom 'Next:Review + create>' button
- Wait until create completes before proceeding with following steps.
Add inbound security rules
Follow this procedure to add inbound security rules:
- Log in to the dashboard.
- Select the 'Virtual machines' item from the left menu.
- The 'Virtual machines' list dialog box appears.
- Select the appropriate virtual machine to add inbound security rules.
- The virtual machine overview dialog box appears.
- Select 'Networking' item from the virtual machine 'Settings' section.
- Click the 'Add inbound port rule' button.
Advanced Networking
TODO
Accessing the FreeSBC
FreeSBC SSH Access
There is no root password by default, you will need to SSH onto the FreeSBC using SSH private key matching the public provided in the SSH public key when #Instantiate a FreeSBC the FreeSBC instance. Login using centos as username.
For example, if your FreeSBC management IP is 192.168.178.30:
> ssh centos@192.168.178.30 ECDSA key fingerprint is 5d:94:a1:93:0f:a4:7a:5d:41:cc:29:49:79:5a:58:f3. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added '192.168.178.30' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts. CentOS-7-x86_64-Minimal-1511/112/190195:197392, Fri 7 Apr 17:41:46 EDT 2017 [centos@freesbc ~]$
Accessing the FreeSBC web portal
- Open a web browser to the management IP of the FreeSBC, on port 12358. Example if your server address is 192.168.178.30, the URL would be:
http://192.168.178.30:12358 - You should get to the FreeSBC Configuration Wizard
From here, you can go to Web Portal Initial Configuration Guide to continue the installation.
Web Portal Initial Configuration
Click on the following link to pursue installation from the web portal: TSBC-SW:WebPortal:Initial Configuration