FreeSBC:SIP Trunking
From TBwiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Configuration) |
(→Configuration) |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
*[[FreeSBC:SIP Trunking:Configuration_A|SIP Trunking Configuration Instruction]] | *[[FreeSBC:SIP Trunking:Configuration_A|SIP Trunking Configuration Instruction]] | ||
*[[FreeSBC Configuration Files:SIP Trunking|SIP Trunking Sample Configuration File]] | *[[FreeSBC Configuration Files:SIP Trunking|SIP Trunking Sample Configuration File]] | ||
| + | *[[Configuring SIP Registration to SIP Proxy|Configuring SIP Registration to SIP Proxy]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 02:37, 15 April 2020
Contents |
SIP Trunking
A SIP Trunk provides the same service you get from a traditional phone lines. The difference is, instead of being a physical wire, a SIP Trunk is a “virtual” line which is provided by a SIP trunk provider delivered over IP using the SIP protocol.
Benefits of SIP Trunking
- Lower circuit costs
- Lower PSTN origination/termination fees
- Better customer service
- Move offices and keep the same number
- Flexibility
- Scalability
- Reliability
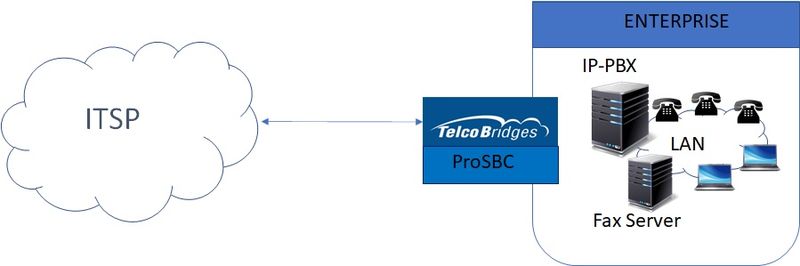
Typical SIP Trunking Sample
Features of the FreeSBC
- Back-to-back user agent (B2BUA)
- DOS/DDOS protection, dynamic blacklisting and call access control
- Easy to deploy, operate and manage through various interfaces including a RESTful API
- Integrated network troubleshooting tools (traces, media/signaling recording, test call generation, etc)
- Up to 60,000 simultaneous signaling and media sessions
- Media transcoding
- Flexible and extensive routing with SIP headers modification capabilities
- Fit to install on virtual machines, clouds, baremetal servers or TelcoBriges' hardware.
Configuration
- SIP Trunking Configuration Instruction
- SIP Trunking Sample Configuration File
- Configuring SIP Registration to SIP Proxy