SIP
(Added RFC4028 Session Timers (see trk#9189)) |
|||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
'''SIP''' | '''SIP''' | ||
| − | + | {| border="1" | |
| − | + | ! Specification | |
| − | + | ! Toolpack Support | |
| − | + | ! Gateway Support | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | RFC 3261 Session Initiate Protocol | |
| − | + | | align="center" | Complete | |
| − | + | | align="center" | Complete | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | RFC 2976 SIP INFO Method | |
| − | + | | align="center" | Complete | |
| − | + | | align="center" | Partial (For DTMF Tones Only) | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | RFC 3398 ISUP-SIP Mapping | ||
| + | | align="center" | Complete | ||
| + | | align="center" | Complete | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | RFC 3515 Refer Method | ||
| + | | align="center" | No | ||
| + | | align="center" | No | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | RFC 3578 Overlap | ||
| + | | align="center" | Partial (Conversion of ISUP Overlap Signalling into SIP en-bloc Signalling) | ||
| + | | align="center" | Partial (Conversion of ISUP Overlap Signalling into SIP en-bloc Signalling) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | RFC 2327 Session Description Protocol | ||
| + | | align="center" | Complete | ||
| + | | align="center" | Complete | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | RFC 3581 An Extension to the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) for Symmetric Response Routing | ||
| + | | align="center" | Complete | ||
| + | | align="center" | Complete | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | RFC 3665 Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Basic Call Flow Examples | ||
| + | | align="center" | Partial | ||
| + | | align="center" | Partial | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | RFC 3666 Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) Call Flows | ||
| + | | align="center" | Complete | ||
| + | | align="center" | Complete | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | RFC 3892 Referred-By Mechanism | ||
| + | | align="center" | No | ||
| + | | align="center" | No | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | RFC 3891 "Replaces" Header | ||
| + | | align="center" | Complete | ||
| + | | align="center" | Complete | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | RFC 4028 Session Timers in the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) | ||
| + | | align="center" | Partial (Refresh May Only Be Done Using UPDATE) | ||
| + | | align="center" | Partial (Refresh May Only Be Done Using UPDATE) | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== Related actions == | == Related actions == | ||
Revision as of 16:52, 21 July 2010
Session Initiation Protocol, more commonly known as SIP, is a signaling protocol for packet-based networks and is commonly used, along with H.323 to provide signaling for voice over IP (VoIP) communications.
Contents |
TelcoBridges and SIP
Toolpack provides support for signaling using the Session Initiation Protocol, more commonly known as SIP, for voice over IP (VoIP) communications. SIP may be used in conjunction with various voice codecs for the media component of a call. TelcoBridges Tmedia media gateways and Tdev development platforms support SIP signaling concurrently with SS7, ISDN and other signaling protocols.
SIP signaling stacks are configured for IP applications and for each Tmedia or Tdev unit requiring SIP signaling.
Based upon your system requirements, you can configure a SIP stack to carry signaling traffic over multiple transport servers, which are IP endpoints comprised of: protocol type (TCP/UDP), port number, IP interface, IP address, IP name, and SAPs.
A conceptual illustration is provided below:
While TelcoBridges media gateways can perform multiple simultaneous functions such as switching and transcoding as well as deliver value-added services such as IVR or conferencing, they can also be configured to perform a single function. In this case, it is possible to configure TelcoBridges media gateway to act as a SIP gateway.
TelcoBridges' SIP Implementation
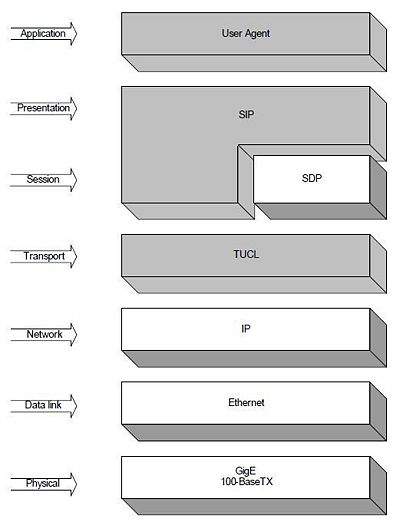
TelcoBridges' SIP implementation works on top of a couple of layers, including SIP and TUCL. In the following figure, grey boxes represent entities that need allocation on the TelcoBridges equipment. The TUCL layer is a transport layer used by SIP on our architecture. TUCL presents some advantages over a simple TCP/IP stack. For instance, it adds tracing facilities to any virtual interface.
Supported SIP RFCs
TelcoBridges supports the following RFCs for SIP:
SIP
| Specification | Toolpack Support | Gateway Support |
|---|---|---|
| RFC 3261 Session Initiate Protocol | Complete | Complete |
| RFC 2976 SIP INFO Method | Complete | Partial (For DTMF Tones Only) |
| RFC 3398 ISUP-SIP Mapping | Complete | Complete |
| RFC 3515 Refer Method | No | No |
| RFC 3578 Overlap | Partial (Conversion of ISUP Overlap Signalling into SIP en-bloc Signalling) | Partial (Conversion of ISUP Overlap Signalling into SIP en-bloc Signalling) |
| RFC 2327 Session Description Protocol | Complete | Complete |
| RFC 3581 An Extension to the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) for Symmetric Response Routing | Complete | Complete |
| RFC 3665 Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Basic Call Flow Examples | Partial | Partial |
| RFC 3666 Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) Call Flows | Complete | Complete |
| RFC 3892 Referred-By Mechanism | No | No |
| RFC 3891 "Replaces" Header | Complete | Complete |
| RFC 4028 Session Timers in the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) | Partial (Refresh May Only Be Done Using UPDATE) | Partial (Refresh May Only Be Done Using UPDATE) |
Related actions
Refer to the appropriate Toolpack release: