Sip registration forwarding
TSBC registration forwarding feature allows to control the registration requests flow between SIP User Agents and registrars. It allows adaptation of SIP register messages between SIP User Agents and registrars. It keeps information about SIP User Agent contacts and allows routing of SIP calls base on registration information.
Contents |
Protection
- TSBC protects registrar from overloading of SIP User Agents register requests using different strategies (i.e. Firewall, Rate Adaptation, SIP Header Manipulation, Etc.).
Forwarding Modes
- The TSBC always modifies the contact URI in SIP register requests to remain on the path between SIP User Agents and registrars.
- The TSBC supports two different SIP registration forwarding modes (i.e. "Contact Remapping" or "Contact Passthrough").
- The "Contact Passthrough" forwarding mode makes contact username portion of the contact URI in SIP register requests to pass through unchanged.
- The "Contact Remapping" forwarding mode modifies contact username portion of the contact URI in SIP register requests and make it unique.
Registrar Selection Mode
- The TSBC supports Active/Standby registrar selection mode. The active registrar is the one with status up and the lowest priority (automatic fallback).
NAT traversal
- The TSBC handles SIP Calls NAT traversal then allows interaction between SIP User Agents from public and private networks.
- It supports SIP register requests "Rate Adaptation" between SIP User Agents and registrar.
- Because refreshing requests are not always sent to registrar, "Rate adaptation" feature reduces SIP register requests sent to registrar. The "Rate Adaptation" feature is also useful to keep firewall ports open.
SIP Calls routing
- The TSBC keeps SIP User Agents contacts information. This information serves on SIP calls routing when a SIP User Agent is trying to reach a registered users. It could be used also to accept calls from registered users only.
Registered users and routing scripts
Registered users can be reached by creating static routes without a specific "outbound NAP". These routes, instead of forwarding calls to a specific NAP, will dynamically choose the outbound NAP by matching the target registered user.
Example:
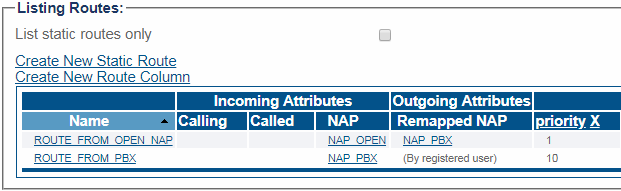
In this example, there are 2 routes:
- ROUTE_FROM_OPEN_NAP will match all incoming calls received from NAP_OPEN, and forward them to NAP_PBX
- ROUTE_FROM_PBX will match all incoming calls received from NAP_PBX, and forward them by registered user (will forward to whatever NAP the target user has registered from)
Here, if "alice" calls "bob" from NAP_OPEN, the call will be forwarded to the PBX. Then the PBX may route back the call to the SBC, which will then forward to "bob" on NAP_OPEN.
In this example, the routes are exclusive (only one will match for a given incoming call). But there could be multiple matching routes. In this case, routes will be ordered by priority (whether they route by registered user, or to a specific outbound NAP).
Configuration
| FreeSBC |
|---|