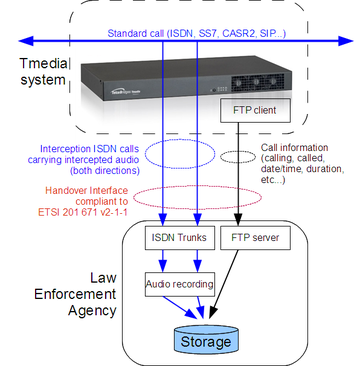
Lawful Interception
A feature provided by service providerss to law enforcement agencies (FBI, Interpol, RCMP, etc.) that allowing law enforcement agencies to intercept calls by receiving a copy of the audio of both parties and call information records.
Contents |
Overview
- Lawful Interception (process of intercepting a target's conversation)
- Interception target (someone under investigation by law enforcement agency, and whom the agency wants to intercept calls)
- Law enforcement agency ( an agency that has, by law, the power to request the interception of calls toward or from targets)
- A law enforcement agency sends, to the service provider, a list of targets to intercept (phone nubers)
- Service provider configures its equipments to intercept the targets, based on phone numbers
- When service provider equipments detect a call that involves a target to intercept, it
- Forwards a copy of call audio (both directions) to the agency through forked calls (CC link - a call toward the agency, carrying intercepted audio)
- Sends information records (IRI records) to the agency)
- Telcobridges supports specification ETSI ES 201 671 v2.1.1 (2001-09), and not CALEA, PCES, and ANSI T1.678
Lawful Interception Requirements
- Detecting target
- Law enforcement agency provides a list of targets (Type of intercepted targets can be from: PSTN, ISDN, GSM (CS), TETRA, GPRS (PD), UMTS (CS))
- LIID (Lawful Intercept Identifier, unique identifier assigned to a target by an agency) for the target
- Phone number of the target
- Start/end date and time for the interception
- Service provider updates targets in its equipment and equipments detect a matching calling or called number, and activates the interception
- Law enforcement agency provides a list of targets (Type of intercepted targets can be from: PSTN, ISDN, GSM (CS), TETRA, GPRS (PD), UMTS (CS))
- Intercepting targets
- In a call, each call leg can be an interception target
- When a leg is an interception target, it's intercepted:
- Audio <<from>> this leg is forked to a new outgoing call
- Audio <<to>> this leg is forked to a new outgoing call
- IRI records are generated for this interception
- Intercepting multiple targets
- Both legs may be independently and simultaneously intercepted
- 2 pairs of forked audio outgoing calls
- 2 sets of IRI records
- Both legs may be independently and simultaneously intercepted
Intercepting Audio
- For each direction (audio <<from>> and <<to>> the target):
- A new outgoing call leg is made, toward the agency
- Audio is <<forke>> (half-duplex joined)
- These outgoing call legs are made toward:
- An outgoing NAP explicitly assigned to the agency
- optionally, using specified calling/called numbers
- Forking does NOT require DSPs
- Audio forking is done as soon as possible
- Immediately for the audio <<from>> the target (this may include even the ring back tone, or may include audio from incoming call during ringing)
- Upon joining with other active leg for the audio <<to>> the target
IRI records
The call data (known as Intercept Related Information or IRI in Europe and Call Data or CD in the US) consists of information about the targeted communications, including destination of a voice call (e.g., called party’s telephone number), source of a call (caller’s phone number), time of the call, duration, etc. Intercept Related Information record (IRI record) is a CDR-style record that contain IRI information on an intercepted call
Types of IRI records
- Start: Indicate that the interception is starting at first event of the communication (attempt)
- Continue: Indicate call state change at any time during the communication (attempt)
- End: Indicate the end of the interception at the end of the communication (attempt)
- Report: For any non-communication related events
Typical information found in an IRI record
- Record type (Start, Continue, End, Report)
- LIID
- CIN (communication identity number)
- Operator identifier
- Direction (target is originating, or terminating)
- Call state (idle, setup, connected)
- Duration of ring and conversation states
- Calling / called party numbers
- Release reason
- CC link state (setup, active, released, lack of resources)
- CC link release reason
IRI records generating
- IRI records are generated at various states of the interception
- They provide information on the interception, and call state
- In a call, each call leg can be an interception target
- When a leg is an interception target, it’s intercepted:
- Audio «from» this leg is forked to a new outgoing call toward the agency
- Audio «to» this leg is forked to a new outgoing call toward the agency
- IRI records are generated for this interception
- Both legs may be independently and simultaneously intercepted
- 2 pairs of forked audio outgoing calls
- 2 sets of IRI records
IRI records encoding
- IRI records are encoded in ASN.1 (a binary encoding standard that is used by IRI records) format
- ASN.1 IDs and objects hierarchy for encoding IRI records is provided by ETSI specifications
IRI records values and files specification
- IRI records values can be
- Mandatory in each record
- In one record only for the whole call
- optional (in some records only, or none at all)
- IRI record files can
- Contain only one IRI record (one file per record)
- Contain multiple IRI records (grouped)
IRI records uploading to the agency
- As files, using the FTP protocol
- Telcobridges also supports SFTP as file transfer method
Configuring Lawful Interception
- Configure Lawful Agencies
- Summary of information required
- NAP to use for CC links
- FTP (or SFTP) server info (IP, port, user, password, folder)
- IRI upload mode (per record, grouped)
- Multiple agencies can be configured
- Note: SFTP requires password-less login to be configured (through exchange of keys between servers)
- Summary of information required
- Provide the list of intercepted targets
- The list of intercepted targets is provided as a CSV file
- Uploaded in the <<File DB>> section of the Web Portal
- Required columns:
- liid
- number
- Optional columns
- start
- end
- Example
- The list of intercepted targets is provided as a CSV file
liid,number,start,end John Smith,555-0001,2012-10-24T00:00:00-05:00,2012-10-24T23:59:59-05:00 Joe Dalton,333-3007,2012-01-01T00:00:00-05:00,2012-12-31T23:59:59-05:00 Ben Laden,022-44-66-33-11 Ben Yi,450-621-1990
- Enable Lawful Interception in routing scripts
- The <<lawful interception.. routing script filter is provided with toolpack
- Users only need to <<include>> it in their current routing script
require 'lawful_intercept'�(...) include LawfulIntercept�(...) after_filter :method => :enable_lawful_intercept
Lawful Interception Statistics
- Live statistics and statistics history
- The Web Portal provides Lawful Interception statistics
- Global
- Per agency
- Availabke statistics are
- Total / current intercepted calls
- Total IRI records generated
- Total IRI records dropped
- Total failed interceptions
- IRI records upload queue length and state
- ... and a few more
- The Web Portal provides Lawful Interception statistics
==Testing Lawful Interception