Toolpack:Configuring Call Trace A
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
| − | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-collapsetext="To search for | + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-collapsetext="To search for calls that are no longer in memory, do the following:" data-expandtext="Searching for calls that are no longer in memory" style="width: 400px;"> |
By default, the system stores up to 10,000 call legs in memory. If the call is no longer in memory, it may be retrieved by using information from the uctdata log files. | By default, the system stores up to 10,000 call legs in memory. If the call is no longer in memory, it may be retrieved by using information from the uctdata log files. | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
* 'p' to print all uctdata files on disk | * 'p' to print all uctdata files on disk | ||
| − | To load a file | + | To load a file into memory for viewing with the Web Portal: <br> |
| − | *Option 'o' | + | * Option 'o' followed by the data filename (uctdata*) |
Use the Web Portal to search for calls using the appropriate filter criteria. The memory will not be overwritten until you restore normal process. | Use the Web Portal to search for calls using the appropriate filter criteria. The memory will not be overwritten until you restore normal process. | ||
Revision as of 17:30, 25 October 2012
Applies to version v2.6
Call Trace is a diagnostic tool that is designed to trace the path a call takes through a Tmedia system, and to provide information about numerous aspects of the call path, such as:
- The routing decision
- The outgoing call
- Subsequent outgoing calls, in the case of a route retry
- Parameters selected for a SIP SDP
- The SIP Call-id
- The trunk and timeslot chosen for TDM protocols
- The termination result code, and more.
A call path is shown as separate call legs, distinguishing the incoming portion with other portions of a call. Call trace enables a default of 10,000 call legs to be stored on the system and be viewed using the Web Portal.
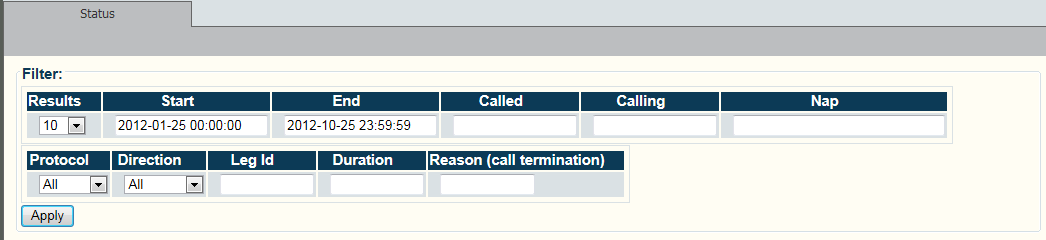
Calls may be filtered by called number, calling number, Network Access Point (NAP), time of day range, protocol and direction.
To configure call trace:
1- Click Call Trace in the navigation panel
2- Set various parameters for the call trace, such as
- Time and date range
- Called or calling number
- Network Access Point (NAP)
- Incoming or outgoing calls
- Call Duration, Reason Code
Once you are satisfied with the filter criteria, click Apply
The filter results are displayed.
3-Select a call in the results window to display further information about the call.
From the web interface:
Applications -> Instances -> Status tab -> tbuctwriter -> Oam target state [Run]
To modify the application configuration (such as the trace level and memory size):
Applications -> Configurations -> tbuctwriter [Edit] Systems -> Activate Configuration
To see logs
From the web interface:
Call Trace
By default, the system stores up to 10,000 call legs in memory. If the call is no longer in memory, it may be retrieved by using information from the uctdata log files.
By default the file is located in the following path:
/lib/tb/toolpack/setup/12358/2.6/apps/tbuctwriter/uctdata*
1- Start tbx_cli_tools_remote 2- Select tbuctwriter 3- To know which files are available, as well as the start and end time of each file, use the following options:
- 'p' to print all uctdata files on disk
To load a file into memory for viewing with the Web Portal:
- Option 'o' followed by the data filename (uctdata*)
Use the Web Portal to search for calls using the appropriate filter criteria. The memory will not be overwritten until you restore normal process.
To restore normal process:
- Option ‘c’ to clear memory
- Option ‘l’ to have calls put in memory again