AudioMixers
From TBwiki
Contents |
Toolpack audio mixers
A mixer is used to mix the audio of multiple sources (call legs, playing audio file, tone generator...)
Typical usage of audio mixers
Audio mixers can be used, among other things, to:
- Build conferences
- Insert background music to a conversation
- Record both sides of the conversation into a single recorded file.
Joining audio source to a mixer
There are 2 ways to join a mixer:
- Join as a listener only
- Join as a speaker. Speakers can be active / or inactive (inactive speakers are not mixed, but monitored for voice activity)
Maximum call legs per mixer
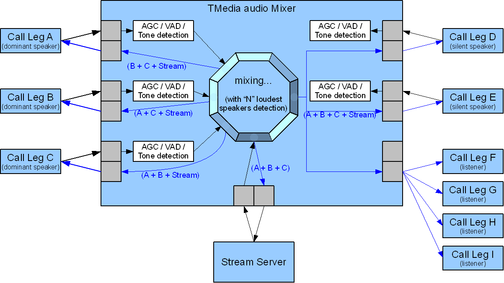
The mixer has the following capabilities:
- The mixer can have any number of listeners (up to maximum number of call legs supported by the TMedia system)
- The mixer can have any number of speakers (up to maximum number of call legs supported by the TMedia system)
- Among these speakers, up to 10 will be considered as "active" (the 10 from which voice was received the most recently)
- Among these 10 active speakers, the audio from dominant N speakers will be mixed (N can be configured per mixer)
Resource usage of mixers
- An active speaker uses one mixer slot (up to 10 per conference)
- All non-active speakers use one mixer slot (although there is no per-conference limit)
- All listeners share the same mixer slot
- IVR on the mixer (playing file, playing tone, recording file) use one mixer slot
TMedia conference capacity
In order to use conferences, TMedia must be equipped with DSPs. Each TMG3200 or TMG7800 unit can be equipped with DSPs for 2,000 conference "slots" (thus a total of 32,000 for TMG7800 system).