Applies to version(s): v2.8.
This article provides the steps required to complete the most common IP network configurations using the Web Portal.
One subnet, Two IP Addresses, Untagged
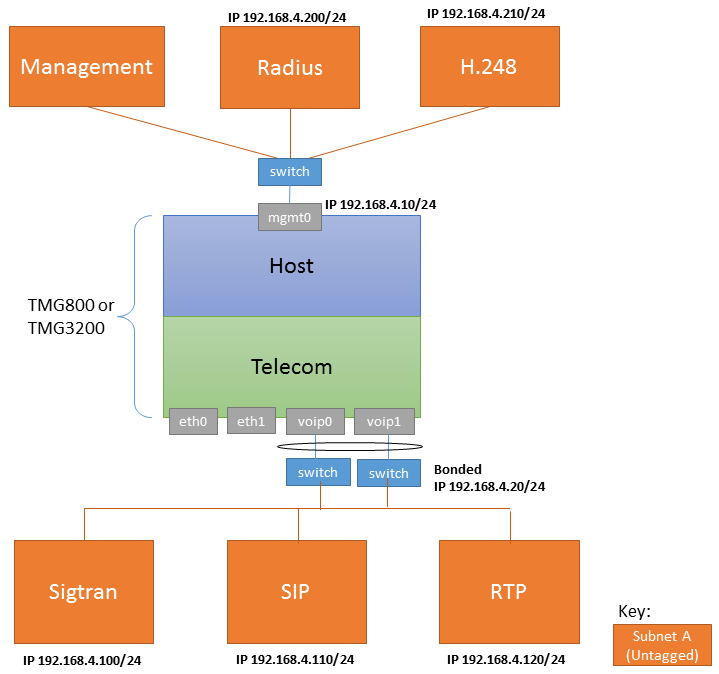
| Configure IP Network A
|
Configure IP Network B
|
|
Subnet A uses the MGMT0 network interface; because it is untagged its IP can only be configured with the tbchangeip command on the SSH port.
|
Subnet B is untagged and bonded over VOIP0 and VOIP1 ports.
When you Create an IP Virtual Port, configure it as follows:
- Name: vp VOIP U
- vLanId: Untagged
- Physical Ports: voip0, voip1
When you Create an IP Address, configure it as follows:
- Name: VOIP_UNTAG
- Virtual Ports: vp VOIP U
IP Address: x.x.x.y
Services: RTP, SIP, SIGTRAN
|
| Configure SIP
|
Configure SIGTRAN
|
Configure H.248
|
Configure RADIUS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Two subnets, One IP per subnet, untagged
[image of network configuration 2]
| Configure IP Network A
|
Configure IP Network B
|
|
Subnet A uses the MGMT0 network interface; because it is untagged its IP can only be configured with the tbchangeip command on the SSH port.
|
Subnet B is untagged and is bonded over VOIP0 and VOIP1 ports.
|
| Configure SIP
|
Configure SIGTRAN
|
Configure H.248
|
Configure RADIUS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Two VLAN, Three IP Address, tagged
[image of network configuration 3]
| Configure IP Network A
|
Configure IP Network B
|
|
|
Subnet B uses untag bonded over VOIP0 and VOIP1 ports
|
| Configure SIP
|
Configure SIGTRAN
|
Configure H.248
|
Configure RADIUS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
