RADIUS
(→TelcoBridges and RADIUS) |
(→Authorization/Authentication) |
||
| (50 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | Remote Authentication Dial In User Service, more popularly known as RADIUS, is used by telecom service providers for the purpose of authenticating, authorizing, and accounting for the use of services by subscribers. A RADIUS server is an application server that provides this functionality. It can take as input as well as output [[Call detail record]] (CDR) data. | + | Remote Authentication Dial In User Service, more popularly known as RADIUS, is used by telecom service providers for the purpose of authenticating, authorizing, and accounting (AAA) for the use of services by subscribers. A RADIUS server is an application server that provides this functionality. It can take as input as well as output [[Call detail record]] (CDR) data. |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== TelcoBridges and RADIUS == | == TelcoBridges and RADIUS == | ||
| − | Starting with release [[Toolpack_version_2.3|v2.3]] of [[Toolpack]], explicit support for the accounting function of RADIUS is now offered. Previously, Toolpack stored [[Call detail record]] (CDR) data in a local database. Starting with Toolpack v2.3, CDR data is stored on a dedicated, external server running an implementation of the RADIUS standard. Configuration of the location of the RADIUS server is performed through the Toolpack web portal. | + | Starting with release [[Toolpack_version_2.3|v2.3]] of [[Toolpack]], explicit support for the accounting function of RADIUS is now offered. Previously, Toolpack stored [[Call detail record]] (CDR) data in a local database. Starting with Toolpack v2.3, CDR data is stored on a dedicated, external server running an implementation of the RADIUS standard. Configuration of the location of the RADIUS server is performed through the Toolpack web portal. |
| + | |||
| + | Starting with release [[TMG-CONTROL_Version_2.6|v2.6]] of [[Toolpack]], multiple RADIUS servers can now be configured for backup purposes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Starting with release [[TMG-CONTROL_Version_2.7|v2.7]] of [[Toolpack]], calls can now be validated through a RADIUS server with authentication and authorization. The RADIUS server may also change routing parameters for calls. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Radius_High-level_drawing_v2.jpg]] | ||
| − | |||
=== Prerequisites === | === Prerequisites === | ||
| − | In order to enable RADIUS functionality in Toolpack, you must have a RADIUS server already up and running. It is highly recommended that the RADIUS server software being running on a separate machine from the one running the Toolpack software. Before configuring Toolpack, you will need the IP address of the RADIUS server(s). You will need to specify a ‘secret key’ which will authenticate the Toolpack server so that it can send | + | In order to enable RADIUS functionality in Toolpack, you must have a RADIUS server already up and running. It is highly recommended that the RADIUS server software being running on a separate machine from the one running the Toolpack software. Before configuring Toolpack, you will need the IP address of the RADIUS server(s). You will need to specify a ‘secret key’ which will authenticate the Toolpack server so that it can send accounting, authentication and authorization data and to the RADIUS server and the RADIUS server will accept it. |
| − | |||
| − | + | == Configuration == | |
| − | === | + | === Accounting === |
| + | *[[Toolpack:Tsbc_CDR_Settings_3.0|Web Portal v3.0: RADIUS configuration]] | ||
| + | *[[Toolpack:CDR_Settings_C|Web Portal v2.10: RADIUS configuration]] | ||
| + | *[[Toolpack:CDR_Settings_B|Web Portal v2.9: RADIUS configuration]] | ||
| + | *[[Toolpack:CDR_Settings_A|Web Portal v2.8: RADIUS configuration]] | ||
| − | + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-collapsetext="other versions" data-expandtext="Click here for other versions" style="width: 400px;"> | |
| − | + | *[[Web_Portal_Tutorial_Guide_v2.7#CDR|Web Portal v2.7: RADIUS configuration]] | |
| − | + | *[[Web_Portal_Tutorial_Guide_v2.6#CDR|Web Portal v2.6: RADIUS configuration]] | |
| − | + | *[[Toolpack:Configuring_RADIUS_A|Toolpack v2.5: RADIUS configuration]] | |
| − | + | *[[Toolpack:Configuring_RADIUS_A|Toolpack v2.4: RADIUS configuration]] | |
| − | + | *[[Toolpack:Configuring_RADIUS_A|Toolpack v2.3: RADIUS configuration]] | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | === Authorization/Authentication === |
| + | *[[Toolpack:Tsbc_Call_Routes_Settings_3.0#RADIUS_Authorization_and_Authentication|Web Portal v3.0: RADIUS Authorization and Authentication configuration]] | ||
| + | *[[Toolpack:Call_Routes_Settings_C#RADIUS_Authorization_and_Authentication|Web Portal v2.10: RADIUS Authorization and Authentication configuration]] | ||
| + | *[[Toolpack:Call_Routes_Settings_B#RADIUS_Authorization_and_Authentication|Web Portal v2.9: RADIUS Authorization and Authentication configuration]] | ||
| + | *[[Toolpack:Call_Routes_Settings_A#RADIUS_Authorization_and_Authentication|Web Portal v2.8: RADIUS Authorization and Authentication configuration]] | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-collapsetext="other versions" data-expandtext="Click here for other versions" style="width: 400px;"> | ||
| + | *[[Web_Portal_Tutorial_Guide_v2.7#RADIUS_Authorization_and_Authentication|Web Portal v2.7: RADIUS Authorization and Authentication configuration]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| − | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RADIUS Wikipedia article] | + | == Authorization == |
| + | |||
| + | If a Radius authorization server is configured, the call authorization is done externally (using the Radius protocol). The acceptance or refusal of the call is then returned into a routing script for further processing. Refer to [[Routing_script_tutorial:Mini_Development_Guide#Authorization | Radius authorization ]] for more details. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == RADIUS Redundancy and Association == | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Radius_Acct_Auth_Redundancy|Radius Accounting and Authentication Redundancy]] | ||
| + | *[[Radius_Acct_Auth_Association|Radius Accounting and Authentication Association]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Toolpack to RADIUS CDR attributes remapping == | ||
| + | When Toolpack sends ''Access-Request'' messages to a RADIUS server, some specific attributes are included in the message. These attributes have been improved through Toolpack releases to better meet accounting services requirements. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== RADIUS CDR attributes list ==== | ||
| + | *[[Toolpack:RADIUS_CDR_attributes_D|Toolpack v3.0 and higher]] | ||
| + | *[[Toolpack:RADIUS_CDR_attributes_C|Toolpack v2.7, v2.8, v2.9, v2.10]] | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" data-collapsetext="other versions" data-expandtext="Click here for other versions" style="width: 400px;"> | ||
| + | *[[Toolpack:RADIUS_CDR_attributes_B|Toolpack v2.6]] | ||
| + | *[[Toolpack:RADIUS_CDR_attributes_A|Toolpack v2.5 and earlier]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Dealing with incoherent CDR entries == | ||
| + | In some situations (during HA switchover for example), some CDR entries may be lost. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following guide lines provide information on how to deal with these corner cases: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Call_Detail_Records_Entry_Loss|Deal with CDR entries loss]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | *[[Toolpack:Status_Menus:RADIUS_A|Radius status in TMG web portal]] | ||
| + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RADIUS Radius Wikipedia article] | ||
| + | *[http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2866.txt Link to RFC 2866 – Radius Accounting] | ||
*[http://www.freeradius.net FreeRADIUS website] | *[http://www.freeradius.net FreeRADIUS website] | ||
[[Category:Glossary]] | [[Category:Glossary]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Revise on Major]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:10, 20 February 2018
Remote Authentication Dial In User Service, more popularly known as RADIUS, is used by telecom service providers for the purpose of authenticating, authorizing, and accounting (AAA) for the use of services by subscribers. A RADIUS server is an application server that provides this functionality. It can take as input as well as output Call detail record (CDR) data.
Contents |
TelcoBridges and RADIUS
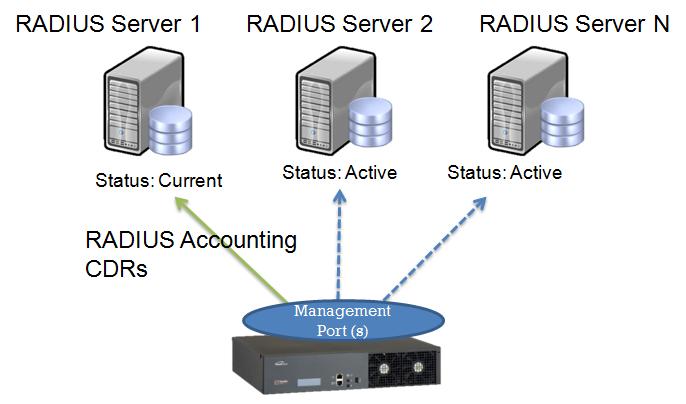
Starting with release v2.3 of Toolpack, explicit support for the accounting function of RADIUS is now offered. Previously, Toolpack stored Call detail record (CDR) data in a local database. Starting with Toolpack v2.3, CDR data is stored on a dedicated, external server running an implementation of the RADIUS standard. Configuration of the location of the RADIUS server is performed through the Toolpack web portal.
Starting with release v2.6 of Toolpack, multiple RADIUS servers can now be configured for backup purposes.
Starting with release v2.7 of Toolpack, calls can now be validated through a RADIUS server with authentication and authorization. The RADIUS server may also change routing parameters for calls.
Prerequisites
In order to enable RADIUS functionality in Toolpack, you must have a RADIUS server already up and running. It is highly recommended that the RADIUS server software being running on a separate machine from the one running the Toolpack software. Before configuring Toolpack, you will need the IP address of the RADIUS server(s). You will need to specify a ‘secret key’ which will authenticate the Toolpack server so that it can send accounting, authentication and authorization data and to the RADIUS server and the RADIUS server will accept it.
Configuration
Accounting
- Web Portal v3.0: RADIUS configuration
- Web Portal v2.10: RADIUS configuration
- Web Portal v2.9: RADIUS configuration
- Web Portal v2.8: RADIUS configuration
Authorization/Authentication
- Web Portal v3.0: RADIUS Authorization and Authentication configuration
- Web Portal v2.10: RADIUS Authorization and Authentication configuration
- Web Portal v2.9: RADIUS Authorization and Authentication configuration
- Web Portal v2.8: RADIUS Authorization and Authentication configuration
Authorization
If a Radius authorization server is configured, the call authorization is done externally (using the Radius protocol). The acceptance or refusal of the call is then returned into a routing script for further processing. Refer to Radius authorization for more details.
RADIUS Redundancy and Association
Toolpack to RADIUS CDR attributes remapping
When Toolpack sends Access-Request messages to a RADIUS server, some specific attributes are included in the message. These attributes have been improved through Toolpack releases to better meet accounting services requirements.
RADIUS CDR attributes list
Dealing with incoherent CDR entries
In some situations (during HA switchover for example), some CDR entries may be lost.
The following guide lines provide information on how to deal with these corner cases: